Introduction:
Custom code in Talend offers a powerful way to enhance batch processing efficiently by allowing developers to implement specialized logic that is not available through Talend’s standard components. This can involve data transformations, custom code as per use case and integration with flat files as per specific project needs. By leveraging custom code, users can optimize performance, improve data quality, and streamline complex batch workflows within their Talend jobs.
Talend Components:
Key components for batch processing as mention below:
- tDBConnection: Establish and manage database connections within a job & allow configuration with single connection to reuse within Talend job.
- tFileInputDelimited: For reading data from flat files.
- tFileRowCount: Reads file row by row to calculate the number of rows.
- tLoop: Executes a task automatically, based on a loop size.
- tHashInput, tHashOutput: For high-speed data transfer and processing within a job. tHashOutput writes data to cache memory, while tHashInput reads from that cached data.
- tFilterRow: For filtering rows from a dataset based on specified.
- tMap: Data transformation allows you to map input data with output data and enables you to perform data filtering, complex data manipulation, typecasting, and multiple input source joins.
- tJavaRow: It can be used as an intermediate component, and we are able to access the input flow and transform the data using custom Java code.
- tJava: It has no input or output data flow & can be used independently to Integrate custom Java code.
- tPreJob, tPostJob: PreJob start the execution before the job & PostJob at the end of the job.
- tDBOutput: Supports wide range of databases & used to write data to various databases.
- tDBCommit:It retains and verifies the alterations applied to a connected database throughout a Talend job, guaranteeing that it permanently records the data changes.
- tDBClose: It explicitly close a database connection that was opened by a tDBConnection component.
- tLogCatcher: It is used in error handling within Talend job for adding runtime logging information. It catches all the exceptions and warnings raised by tWarn and tDie components during Talend job execution.
- tLogRow: It is employed in error handling to display data or keep track of processed data in the run console.
- tDie: We can stop the job execution explicitly if it fails. In addition, we can create a customized warning message and exit code.
Workflow with example:
To process the bulk of data in Talend, we can implement batch processing to efficiently process flat file data within a minimal execution time. We can read the flat file data & after the execution, we can process it to insert it into MySQL database table as a target & we can achieve this without batch processing. But this data flow will take quite a longer time to execute. If we use batch processing using the custom code, it takes minimal execution time to write the entire source file data into batch of records into MySQL database table at the target location.
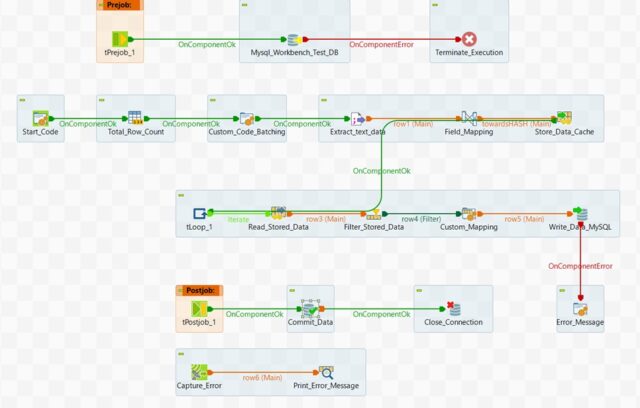
Talend Job Design
Solution:
- Establish the database connection at the start of the execution so that we can reuse.
- Read the number of rows in the source flat file using tFileRowCount component.
- To determine the batch size, subtract the header count from the total row count and then divide the number by the total batch size. Take the whole number nearby which indicates the total number of batch or chunk.
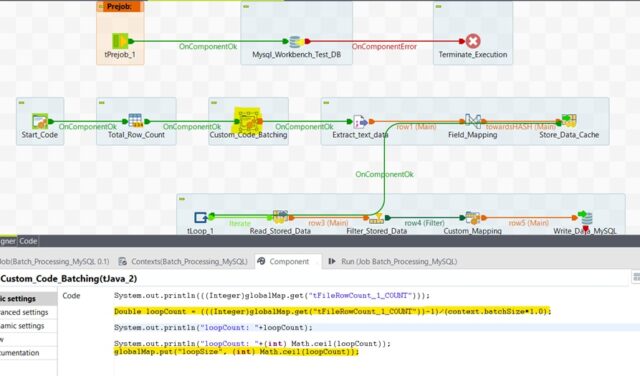
Calculate the batch size from total row count
- Now use tFileInputDelimited component to read the source file content. In the tMap component, utilize the sequence Talend function to generate row numbers for your data mapping and transformation tasks. Then, load all of the data into the tHashOutput component, which stores the data into a cache.
- Iterate the loop based on the calculated whole number using tLoop
- Retrieve all the data from tHashInput component.
- Filter the dataset retrieved from tHashInput component based on the rowNo column in the schema using tFilterRow
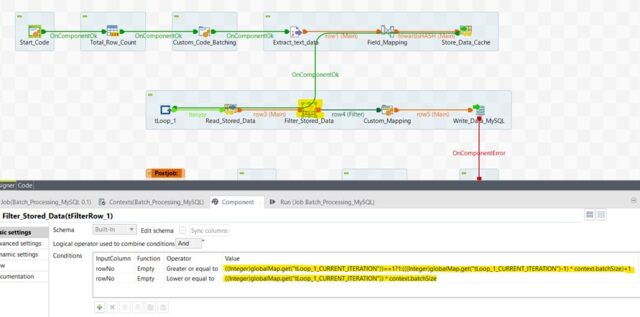
Filter the dataset using tFilterRow
- If First Iteration is in progress & batch size is 100 then rowNo range will be as 1 to 100.
If Third Iteration is in progress & batch size is 100 then rowNo range will be as 201 to 300.
For example, if the value of current iteration is 3 then [(3-1=2)* 100]+1 = 201 & [3*100=300]. So final dataset range for the 3rd iteration will be 201 to 300. - Finally extract the dataset range between the rowNo column & write the batch data MySQL database table using tDBOutput
- The system uses the tLogCatcher component for error management by capturing runtime logging details, including warning or exception messages, and employs tLogRow to display the information in the execution console.
- Regarding performance tuning, tMap component that maps source data to output data, allows for complex data transformation, and offers unique join, first join, and all other join options for looking up data within the tMap component.
- The temporary data that the tHashInput & tHashOutput components store in cache memory enhances runtime performance.
- At the end of the job execution, we are committing the database modification & closing the connection to release the database resource.
Advantages of Batch Processing:
- Batch processing can efficiently handle large datasets.
- It takes minimal time to process the data even after data transformation.
- By grouping records from a large dataset and processing them as a single unit, it can be highly beneficial for improving performance.
- With the batch processing, it can easily scale to accommodate growing data volumes.
- It is particularly useful for operations like generating reports, performing data integration, and executing complex transformations on large datasets.
For more details: Get-started-talend-open-studio-data-integration



This is an excellent continuation! The clear examples and practical tips make mastering custom batch processing in Talend much easier and more efficient.
Amazing post! I really liked how you explained the role of content marketing in building trust. At Bright Pixel Media (https://brightpixelmedia.world/
), we also focus heavily on content-driven strategies, and the results have been fantastic for local businesses. https://brightpixelmedia.world/best-digital-marketing-agency-in-dashrath-puri-bright-pixel-media/
Thanks for the kind words! So glad to hear you found the tips for Talend batch processing helpful. Happy coding!