Better Lead Scoring = Better Conversations
Show me a sales team that has the spare time to decipher ambiguous MQLs worthy of attention, and I’ll show you a double rainbow. Can it happen? Yes. Does it happen often? Hardly.
Insert: Adobe Marketo Engage lead scoring that goes beyond a basic configuration.
When it comes to Marketo, the power to configure basic lead scoring principles such as ‘one email open’ = ‘one positive lead score’ is easy to do. But, taking the time to go beyond prototypical lead scoring in ways that sharpen conversations between sales and prospects is worth its weight in gold.
Effective Marketo instances act on a wide variety of attributes such as demographic, behavioral, and firmographic data points to build useful MQL (marketing qualified lead) profiles.
Spoiler alert: developing a more advanced Marketo lead scoring schema involves a tango between two; Marketo users that dance with sales personnel to gather inputs that guide how qualified leads should manifest.
Go Beyond Basic Lead Scoring
Evaluating leads merely on metrics such as email clicks or opens inevitably produces pseudo-qualified leads. Here are some of the deeper aspects to Marketo lead scoring one should take into account:
Explicit Versus Implicit Data
Explicit data is information that can dictate lead scoring based upon aspects such as industry, geography, job title, level of decision-making, or specific company. These are relevant, quantifiable data points in which true/falses, yes’/no’s, or clear-cut data points can be defined.
Some advanced explicit factors to consider:
- Does the lead’s job title have access to a measurable budget?
- Do the lead’s geographical characteristics match with how you can offer them a product/service?
- Is the lead’s budget likely to be congruent with your product/service pricing?
On the other hand, implicit data is much more fluid in nature. Implicit data points typically involve interpretations such as product preferences, deliverability needs, or solutions to their problem. Implicit data can even go as far as to measure how content is ingested or which type of content is desired.
Some advanced implicit factors to consider:
- What is the observed readiness to purchase?
- What are the barriers to disseminating product/service information across all stakeholders?
- Is there a specific type of content that resonates with a particular decision-maker?
Active Versus Passive Behavior
For lead scoring, active behavior measures the potential to buy, based upon measurable activities showing sales readiness.
Examples of active behavior:
- Downloaded a sample RFP
- Visited a pricing page
- Watched a product demo video
Passive behavior recognizes the browsing type of engagement activity on a lower scale.
Examples of passive behavior:
- Registered for a webinar
- Viewed home webpage
There becomes a discernable difference between an inquiry of specific prices (active) versus viewing product/service capabilities (passive).
Keeping both behaviors in mind, creating a scoring token system that gives confidence to active versus passive behavior will dictate the fidelity of lead scoring.
Leveling Up Lead Scoring
At times, symbolized lead score leveling can initiate CRM automation to alert the rise or fall of lead scores.
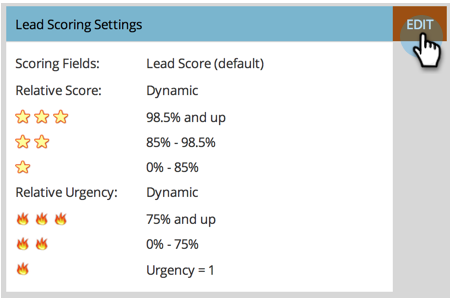
Gather
Marketo users can’t always read the brains of sales. As such, it becomes difficult to gather the climate as to what certifies a lead as ‘sales-ready’. Aggregating said information to disseminate who, what, when, where, and how MQLs onto sales is part and parcel.
Here are some questions that Marketo users can ask that will bridge that gap:
- What data is typically missing that would help the selling process?
- What is the average time in which a lead exists in each stage of the sales cycle?
- Is there specific data that can inform sales of past interactions?
- What purchases were made by the prospect in the past?
- Exactly which past opportunities were missed?
Assign
After an amalgamation of all data points above, it becomes necessary to assign scoring tokens to each. Take the time to implement which scoring tokens are the most important, followed by an iterative evaluation of how they come to fruition in informing sales.
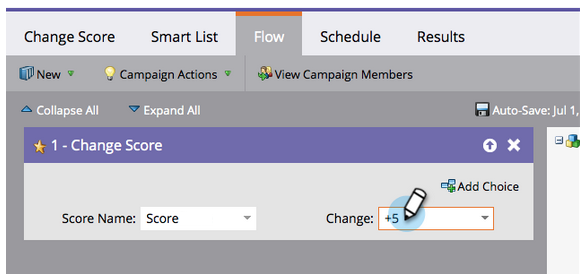
Don’t forget about the importance of negative, or degradation, scoring. Leads can choose an alternative product/service or simply lose interest. Is there potential for recycling? Account accordingly.
{{my.Basic Lead Scoring}} +100
At the conclusion of launching a more advanced lead scoring program, interact with sales to determine results. The act of checking in with sales teams on a continuous basis ensures the evolution of an iterative lead scoring model.
Taking the extra steps to measure and score leads beyond basic measurements will always lead to better conversations between sales and leads.
Seeking help with more advanced lead scoring or something much more complicated? Reach out to the Perficient team to uncover how we can help you and your organization with marketing automation.

