Oracle Cloud OM Business Rules are a great way to take the wheel and drive your business. They provide great flexibility and can help take the drudgery and human factors out of decision making. The best thing about them is that in most cases you don’t have to make modifications or create extensions to make things happen. There is flexibility right out of the box to address most business issues and practices.
Overview of Oracle Cloud OM Business Rules
You can use Oracle Cloud OM Business rules to transform Orders, Transform Products, assign Orchestration Processes, route orders to different fulfillment systems and serve as a tool to manage orders.
They come in a number of varieties and serve different purposes. OM rules are created one of two methods; the Oracle Business Rule engine or the Visual Builder. Oracle Business Rules is the more complex platform and it may require experienced Technical Developers to achieve complex rules. Visual Builder is as the name implies visual object based in its approach.
Transform with Oracle Cloud OM Business Rules
Use Rules to modify Orders either before order transformation (Pre-transformation) or after (Post Transformation). In addition, a user can transform the item(s) with Product Transformation rules.
Pre-Transformation
If you’re familiar with Oracle Order Management in EBS, Pre-transformation rules are the equivalent to defaulting rules. They can be used to default just about any Sales Order field based on an attribute or attributes.
Some Examples of possible Pre-Transformation rule uses are :
- Setting the Payables Transaction Type based on Order Type or Line Type
- Defaulting a Salesperson based on an Order Source
-
Set Ship Method based on order type or item class
-
Set the line type based on an item attribute.
Users can create Pre-transformation rules using either the Oracle Business Rules or the Visual Builder tools.
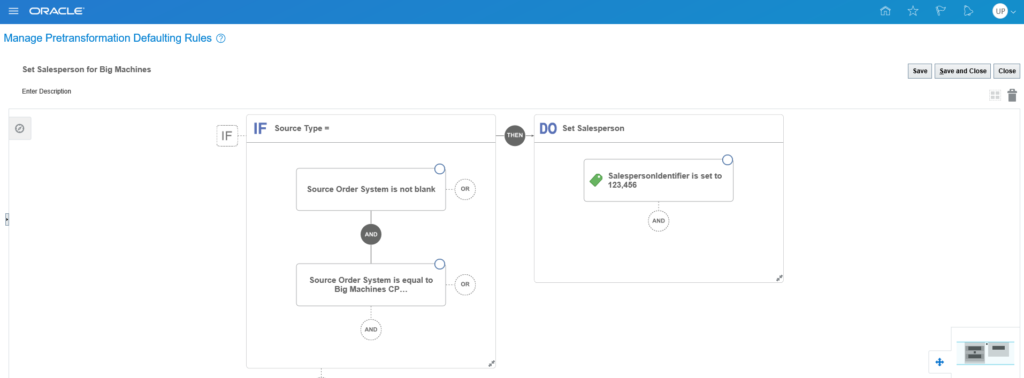
Example Pre-Transformation Rule using Visual Builder
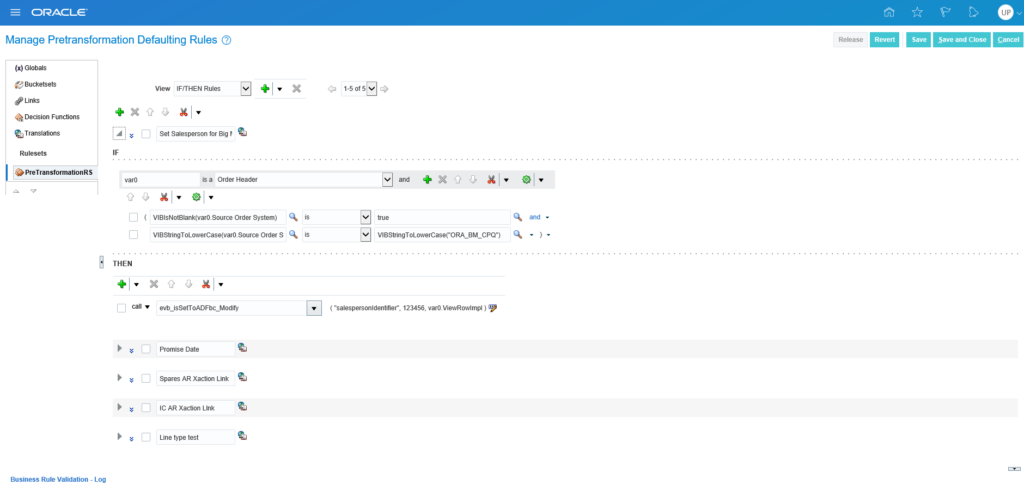
Example – Pre-Transformation Rule using Oracle Business Rules
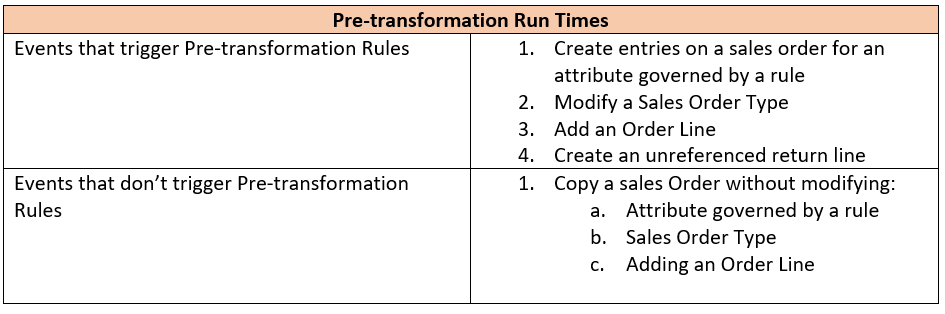
Product Transformation
Does your business have products are complicated or have sales relationships between them? You can use Product Transformation rules to control the configuration or combinations of items that you ship. Product Transformation allows the creation of rules to control items that ship together, prohibit certain items from going to certain places (in the absence of GTM) or even to reward customers with a gift for purchases of certain items or quantities
Some use cases for Product Transformation Rules:
- Enforce shipment of the correct power adapter for a laptop based on product or ship to country/region
- Ensure that a piece of equipment ships with order lines that ship the necessary tools, documentation or auxiliary equipment to operate the equipment
- Prohibit the shipment of certain components with a product based on incompatibility
- Automatically delete related items from a sales order if a main component item is deleted from the order.
- Reward a customer for an order quantity with a bonus item or items.
You write Product Transformation Rules using the Oracle Business Rule engine (as of this writing there is not an option to use Visual Builder). Product Transformation rules are a little more complex to write. This is because the driver for item identification in the engine is the Item ID and not the item number. This necessitates the use of Bucket Sets to act as translators between the CSR world and the system. You might need to create a rules dictionary to help achieve your end goal.
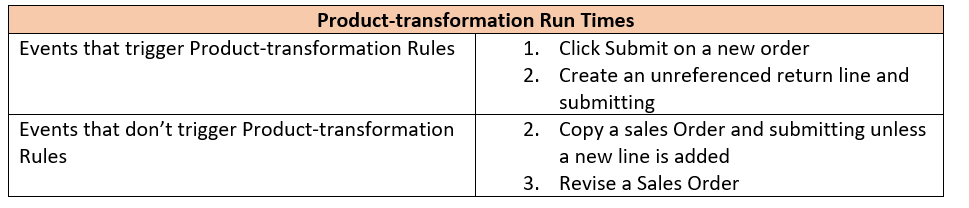
Post Transformation
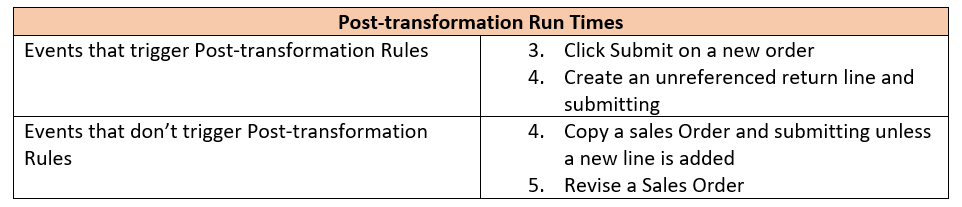
You can write Post Transformation rules make changes to Sales Orders between Transformation and submission to the fulfillment system. Post-transformation rules allow you to deal with attributes that may change or are not yet set at Transformation time. This includes attributes such as dates or finalized products in the sales order lines.
The need for Post Transformation can widely vary from business to business and as such have a wide range of uses such as defaulting dates, changing date formats, changing warehouses by item.
Some of the attributes available for use with Post Transformation Rules
Post-Transformation rules are very complex. As such, it takes a fair amount of practice to get completely familiar with them. Technical staff can create Post Transformation Rules using the Oracle Business Rules engine. OBR allows the use of Bucket Sets and Dictionaries that can be defined for your purposes.
Assign with Oracle Cloud OM Business Rules
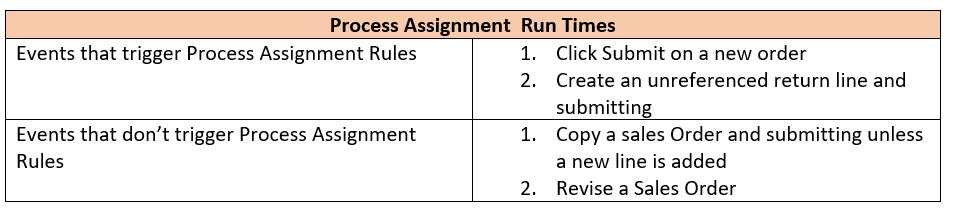
Process Assignment
Oracle Order Management rides on something known as Order Orchestration Processes (Look for future writings on this subject). The Orchestration Process performs the same function as the Workflows do in Oracle EBS. They route orders to the correct paths for fulfillment or other order functions.
A developer can create Custom Orchestration processes to suit your business needs. Process Assignment Rules are a means of linking your custom orchestration processes (or controlling standard processes) to specific events or conditions.
Processes can be assigned based on a number of attributes, Some Examples are:
- Customer
- Destination
- Item Quantity
- Item/Item Category
- Carrier
- Order Line Type.
User have a choice of either the Visual Builder or Oracle Business Rules engines to design Process Assignment Rules.
Route with Oracle Cloud OM Business Rules
Routing Rules
If your business is supported by multiple fulfillment systems, You can create rules to route fulfillment lines to the appropriate system(s). Using Routing rules can avoid manual processes in fulfillment such as export from Fusion and uploading to another system.
Routing Rules work in conjunction with Orchestration to send fulfillment lines where they are best fulfilled. For example, you may run a business line that is manufactured to order but are running some manufacturing software other than Oracle Cloud Manufacturing. If the products are shipped directly to the customer from the plant, a routing rule is handy. Routing rules would allow you to send the order lines to the manufacturing software via an interface rather than some other more time intensive process.
You can use either Oracle Business Rules or Visual Builder to create Routing Rules.
Orchestrate with Oracle Cloud OM Business Rules
Orchestration Process Rules
Orchestrations require rules to be defined in order to make certain parts of the process function the way the business needs them to work. These rules are similar in nature to Post Transformation Rules in that they can be very complex and need some planning to create an effective rule.
Some things about Orchestrations are the Line Selection Criteria, Lead Time Expression, Change Compensation behavior and Pause.
For Example, Your company ships the same item from different warehouses based on availability. You can write a lead time rule that considers the location of the warehouse and location of the customer.
It is very important that rules on seeded Orchestrations do not get modified. If you need a rule change to change the behavior of an Orchestration Process, copy an existing seeded orchestration and modify that.
Approve with Oracle Cloud OM Business Rules
Sales Order Approval Rules
Oracle recognized the need for control over sales orders in the Cloud and developed the Sales Order Approval process. Sales Order Approval Rules give a business more control over what happens to a sales order doesn’t meet the rule. They provides a range of options for action from automatic rejection to approval processes based on an individual, a group or a hierarchy. Also, Sales Order Rules can also be used to provide warnings to users if the sales order doesn’t conform to defined characteristics.
SO Approval Rules can be used for many situations, here are some examples;
- Managing Price Overrides
2. Managing Order Totals
a. Order Minimums
b. Order Totals
- Disallowing certain types of Discounts
4. Require Alerts or Approvals for a given source system or systems
Sales Order Approval rules are triggered at submission of the draft sales order. If an order requires approval Oracle sets the status ‘Pending Approval’. So no further processing of the order can take place until the approver(s) approve the order. If an approver rejects the order, then the order status reverts to ‘Draft’. Then the creator can adjust the order to meet parameters.
Use either the Oracle Business Rules Engine or the Visual Builder to build Approval Rules.
Conclusion
Oracle Cloud OM Business Rules provide flexibility, and control. They allow the Order Management Cloud to conform to your needs without having to resort to extensions or manual workarounds to manage your orders. They provide the flexibility to meet business needs when it comes to managing sales orders. In addition, they can be fairly simple to write. If necessary, your technical staff can use the Oracle Business Rule engine to handle more complex rules.
For more about Oracle Fusion Business Rules check this out: https://blogs.perficient.com/2021/02/04/7-best-practices-for-oracle-fusion-business-rules/
For more detailed information about Oracle Cloud OM Business Rules, try this link: https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/saas/supply-chain-management/21a/faiom/orchestrate-fulfillment.html#FAIOM1702198


Can you please let me know how to write a code for “Enforce shipment of the correct power adapter for a laptop based on product or ship to country/region” using product transformation rule?