On 25th May 2018, everybody woke up to find their inbox “spammed” with mails from companies about redefining their data privacy policies containing the term GDPR. Every site that one logged into had a pop up, “We have updated our Data Privacy Policy”. So, what is this all about?
Small Word, Big Impact
It is all about the tiny four letter word ‘G- D- P -R’ which could cost a company millions.
Yes, you read that right.
GDPR which stands for General Data Protection Regulation, has replaced the existing Data Protection Directive rules. It aims to set uniform data privacy rules to provide all the European Union (EU) citizens the right to their personal data. While customers are happy, the companies need to worry. Now companies must redefine ways they gather and store customer information. GDPR is applies to all companies that deal with any EU citizen’s data, irrespective of their location. If one fails to comply, it could cost them 4% of their annual global turnover or 20 million Euros, whichever of the either is the highest.
PII – Data Protection
Personal data (PII – Personally Identifiable Information) refers to any information which leads to the identification of an individual data subject. Third parties use customer data to draw new insights and to study marketing trends. This data undergoes various actions and it is termed as ‘processed data’. Effective data protection techniques when applied to personal data, makes it secure.
The purpose of data protection is to assist ‘data processors’ in remaining compliant. Nowhere GDPR Articles mention that encryption is necessary but implementing such measures can reduce the occurrence of a data breach. In the event of a breach, one need not inform the data subjects if proper data protection measures have been applied. This is applicable only if the data is insufficient to zero down on an individual. Though the respective organization must inform the Data Protection Officer (DPO) at the earliest.
GDPR Compliant Encryption Methods
Depending upon the degree of risk and method of data processing, one can choose the preferred data protection technique. Article 32 of GDPR states that an organization shall implement ideal technical and organizational measures so that data can be secure. The two most commonly stated GDPR-compliant encryption methods mentioned in the GDPR Articles are as follows,
1. Pseudonymization
2. Standard Encryption
Pseudonymization
The method of processing personal data in such a way that the data can no longer be attributed to a specific data subject without the use of additional information is known as pseudonymization. The organization stores this “additional information” at a secure location. The method encodes the personal data with pseudo-random code hence the name pseudonymization.
It is known as “false” anonymization because it can help to re-identify an individual. Anonymization is irreversible and it cannot help relate back to the individual. Unlike anonymization, pseudonymization does not remove all the identifying information from the data. It merely reduces the linkability of data with the individual’s identity. Pseudonymization is the preferred method to re-identify users in the future.
In the below example, John Rhodes is the data subject whose personal data is to be stored in a secure manner. The details which can help to narrow down on John are to be placed in a secure, restricted area.
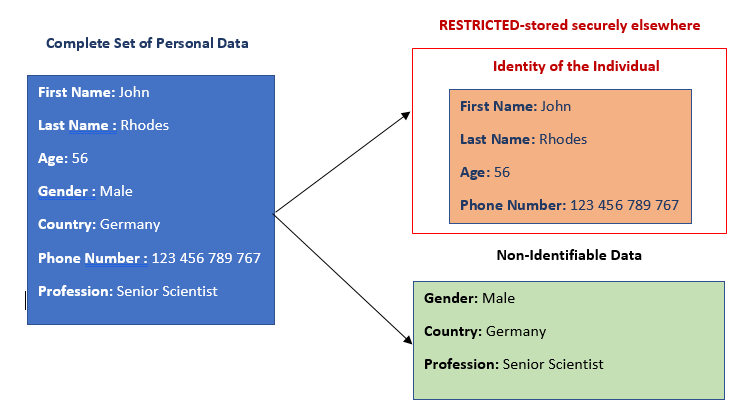
Data Masking is a standard solution for data pseudonymization. This method covers part of the data by random characters or other data. As a result, the data handlers can now use the masked data without any compromise on an individual’s identity. In the below example, data masking masks the important data that helps identify the individual.
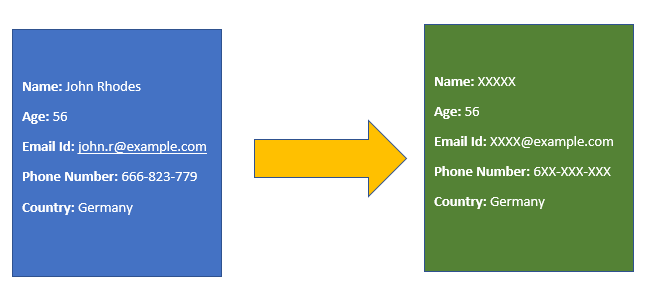
There are a few issues with respect to this data protection technique. Pseudonymous data leads to some form of re-identification after certain amount of reasoning and analysis. Hence the pattern must be subject to change on a regular basis to maintain the integrity and security of data. Even the limited, unrelatable data is available to a large part of the audience with no restriction to data accessibility.
Standard Encryption
Encryption translates data into another form that is unintelligible to any person not authorized to it. An authorized person needs a valid decryption key to decipher the encrypted data thus making encryption an effective data protection method.
There are two major data encryption schemes,
a. Symmetric Encryption
b. Asymmetric Encryption
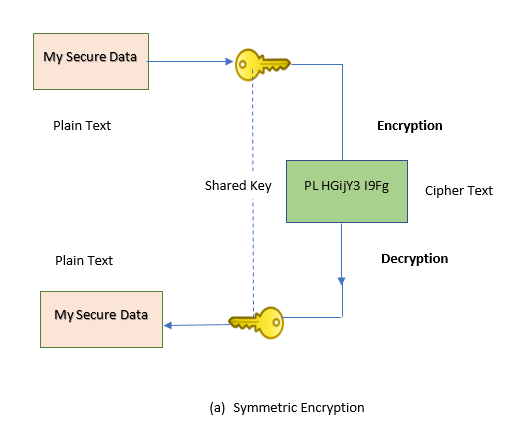
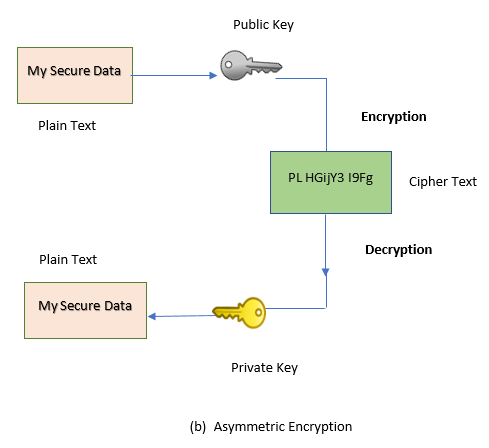
In symmetric encryption, both the involved parties share a common key to access the data. In contrast, asymmetric encryption eliminates the need of sharing a common key by using a pair of public-private keys. It is rarely opted by many since it is much slower than symmetric encryption.
Unlike pseudonymization, only members who own the decryption key, have access to the data thus maintaining the integrity of data. This makes encryption a better choice compared to the former.
On the contrary, data encryption has its share of problems. Upon handling encrypted data, one cannot perform search operations prior to its decryption. The responsible individuals must store the keys used for encryption and decryption in a safe, secure place since losing the keys means losing the data.
Conclusion
It is most common that the first question put forth to a company after a breach is whether the organization has implemented data protection methods. Neglecting data protection can cost one, millions of dollars. Therefore, considering the importance of data privacy, it is always better to be safe than sorry.

