Target audience: Mid to Highly skilled Linux, MQ/IIB and AWS admins.
IBM MQ and IIB have 2 distinct HA Architectures. MQ and IIB can be configured to have an Active Standby(2 live server) or an Active Passive(1 live server) HA configuration. Both MQ/IIB HA designs are publish documents. This article focuses on using just the IBM software and AWS components.
Again, these are high-level design and the details will need to be worked out with a specific client. Internet domains, SSL/TLS and certs are not cover, these items will also need to be incorporated to the client’s specifications.
The picture below depicts a MQ/IIB multi-instance Active Standby HA configuration.
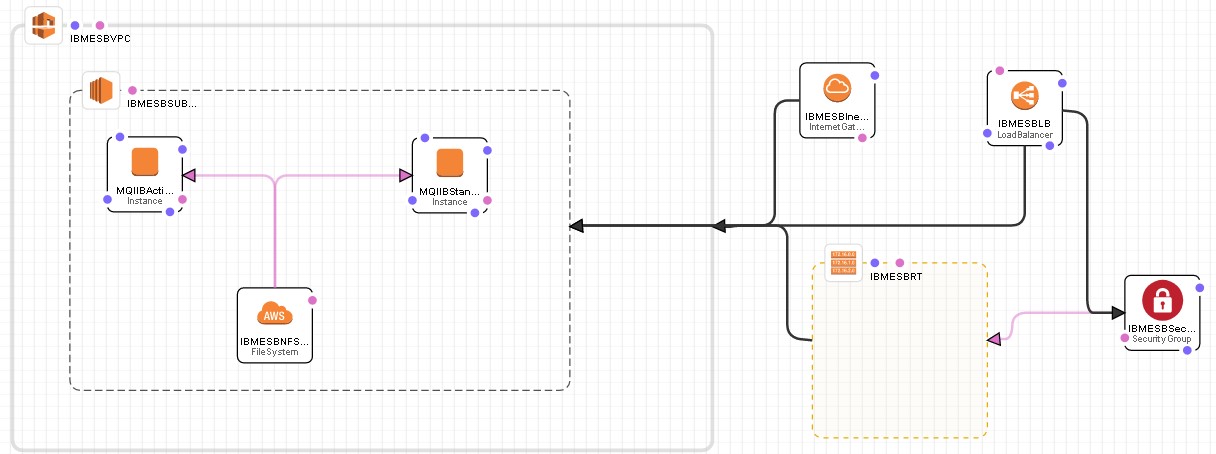
Create the MQ/IIB environment on AWS – Multi-instance(active/standby):
- Create a VPC for MQ/IIB that has a public subnet, Internet Gateway, Security Group, Network ACLs and Routing Table. These AWS components will be created and configure to a client’s specifications. The Security Group and Network ACLs should include MQ/IIB ports and should limit who can get to the MQ/IIB from the internet.
- Create an instance of one of the AWS AMI’s that meets the client’s virtual machine speciation’s.
- Upload the MQ/IIB software to the current AMI instance.
- Install MQ/IIB. Do not define any Queue Managers(QMgr) or Brokers(Brkr).
- Create an AWS EFS file system and mount it to the current AMI instance.
- Set up the /etc/fstab so the EFS NFSv4 file system mounts on bootup.
- Then save that AMI as a custom IBMESB base AMI. This will be the AMI you select as you model the MQ/IIB HA Environment.
- Use the IBMESB base AMI create a second instance in the VPC.
- Now create a QMgr multi-instance configuration on the 2 EC2 servers. Follow the IBM info center for these steps.
- Now create an IIB multi-instance configuration on the 2 EC2 servers. Follow the IBM info center for these steps.
- Start either MQ/IIB instance so it will be the active server. Then start the other MQ/IIB instance as the standby.
- Now create a Load Balance that will monitor and route traffic to the active MQ/IIB server.
- Create a notification even to inform IT support when a failover as occurred.
- Test your new MQ/IIB multi-instance HA environment.
The picture below depicts a MQ/IIB Active Passive HA configuration.
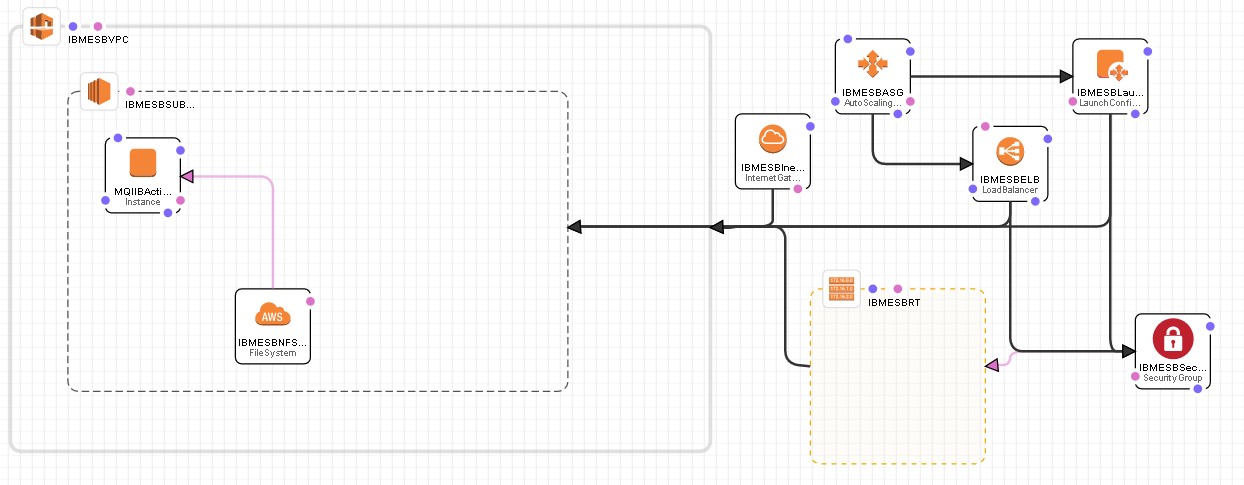
Create the MQ/IIB environment on AWS – Active Passive:
Other references for this design are listed below. Again, this article focuses on using just the IBM software and the tools available in AWS.
- Create a VPC for MQ/IIB that has a public subnet, Internet Gateway, Security Group, Network ACLs and Routing Table. These AWS components will be created and configure to a client’s specifications. The Security Group and Network ACLs should include MQ/IIB ports and should limit who can get to the MQ/IIB from the internet.
- Create an instance of one of the AWS AMI’s that meets the client’s virtual machine speciation’s.
- Upload the MQ/IIB software to it.
- Install MQ/IIB, do not define any Queue Managers(QMgr) or Brokers(Brkr).
- Create an AWS EFS file system and mount it to the current AMI instance.
- Set up the /etc/fstab so the EFS NFSv4 file system mounts on bootup.
- Then save that AMI as a custom IBMESB base AMI. This will be the AMI you select as you model the MQ/IIB HA Environment.
- Now create a QMgr configuration on the EC2 server. Follow the IBM info center for these steps. Put all Qmgr files on the AWS EFS file system.
- Now create an IIB configuration on the EC2 server. Follow the IBM info center for these steps. Put all Brkr files on the AWS EFS file system.
- Now write a script.
- The script will execute at bootup. Call it ESB_startup.
- It will start the QMgr and Brkr.
- Put ESB_startup script in /etc/init.d
- chmod 755 /etc/init.d/ESB_startup
- chkconfig –add ESB_startup
- chkconfig ESB_startup on
- Check it: chkconfig –list ESB_startup
- Now save this instance as your IBMESBRT AMI.
- Now reboot the Instance to see your script work. If both QMgr and Brkr startup, then continue. Otherwise go back to step 10 and debug your script.
- Now delete the current IBMESBRT instance.
- Now create a Launch Configuration/Auto Scaling Group and use the IBMESBRT AMI for the instance.
- The auto scaling group will be a scaling group of 1.
- Start the Launch Configuration
- Now create an Elastic Load Balance for the IBMESBRT instance .
- Add the IBMESBRT Instance and have it monitor the Qmgr Listener. This port numbers will vary if the client chooses not to use standard MQ Listener port.
- Modify the Auto Scaling Group to use the Elastic Load Balancer as its health check.
- Test your configuration by shutting down the Qmgr. You should see the Auto Scaling Group destroy the current instance and spin up a new instance of the Qmgr and Brkr.
References:
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/community/blogs/messaging/entry/mq_openstack_part1_packer?lang=en
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/community/blogs/messaging/entry/mq_openstack_part2_heat?lang=en
