What is Cypress?
Cypress automation is the latest front-end testing standard that every developer and QA engineer should know about. It is a cutting-edge front-end automated testing solution for modern web applications.
Cypress is mainly used for:
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- End-to-End flow Testing
Nonetheless, it can be used for functional testing as well.
Although Cypress is frequently compared to Selenium, the two are fundamentally and structurally distinct.
The nice part is that we can get rid of those Browser Drivers in Cypress 🤩.
Why Cypress and How it is different from Selenium? Magical Spells of Cypress….
- Fast, Consistent, Effortless, and Reliable: In comparison to the Selenium tool, Cypress delivers faster, consistent, effortless, and reliable test execution due to its architectural design, as the test runs directly inside the browser without the use of a browser driver.
- Automatic Waiting: There’s no need to include Waits and Sleep in your tests. Cypress automatically waits for commands and assertions. There will be no more asynchronization.
- Time Travel: We can hover over each command in the Command Log to see exactly what happened at each step. In contrast to other automation tools, we can see and debug each step in the log while the tests are running.
- Easy debugging: Cypress’s Developer Tools make debugging simple. Debugging is quick and painless thanks to the errors and stack trace. The error messages are very readable and explain why our script failed.
- Cypress has a test status menu that displays the number of test cases that have passed or failed.
- Cypress reloads all updates made in the tests by default.
- Screenshot and Videos: By default, Cypress can capture screenshots in the event of a failure. It can also record videos of the entire test suite running from the command line interface. When we run our tests from the Cypress Dashboard, we can watch videos of the entire process.
- Single easy universal Language: Because its architecture is based on Node JS, it only works with JavaScript, which is very simple to learn. JavaScript is extremely simple to work with for both developers and testers.
- Multiple browser support: It supports Chrome, Edge, Electron (default browser comes with Cypress and it run in headless mode) and Firefox (Still in under construction).
- API Testing support: Cypress can perform HTTP calls; thus, we can test APIs as well.
- External Plugin supports: Cypress supports external plugins to widen the test coverage.
Prerequisite and Setup:
Cypress makes it quick and easy to start testing.
We can get Cypress ready to work in two ways:
- Desktop application, which allows us to directly download and install the Cypress application.
- By using Node js NPM and VS code we can start writing our test.
Cypress is a Node.js application that comes packaged as an NPM (Node package Manager) module.
Because it is built on Node.js, it uses JavaScript to write tests, but 90% of the coding can be done using Cypress inbuilt commands that are simple to understand.
Click on the images below to download Node JS and Visual Studio Code (VS Code).
Project Structure after Cypress Installation:
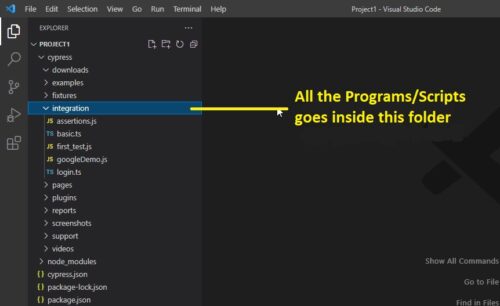
Cypress Framework:
All Cypress tests will be run in a recommended framework known as “Mocha.” It will be bundled with Cypress, so there will be no need to download it separately.
There is another one, “Jasmine”.
Cypress global commands:
‘cy’ is a global command to invoke all the cypress command just like a ‘driver.findElement()’ etc. we call all the required methods.
No need to create or import anything for ‘cy’.
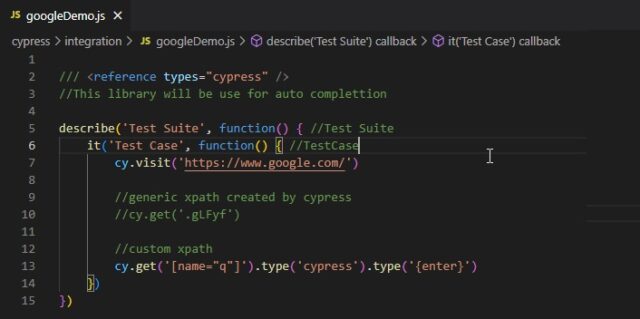
Cypress Test:
As we will be working on JavaScript, so we need ‘.js’ files to write our automation scripts.
In Mocha or Jasmine, we can use ‘describe’ and ‘it’ block to start writing our test.
The ‘describe’ block will be called as test suite.
All the test goes inside this suite.
Cypress assertions:
Just like a TestNG we can also use assertions here to validate the test cases.
Implicit Assertions –
- .should(‘contain’, ”)
- .should(‘have.text’, ”)
- .should(‘be.visible’)
Explicit Assertions –
- expect(‘name’).to.be.equal(‘cypress’)
Assert –
- assert.equal(4, 5, ‘Not equal’)
- assert.notEqual(4, 5, ‘Not equal’)
- assert.isAbove(4, 5, ‘Not equal’)
- assert.isExist(4, 5, ‘Not equal’)
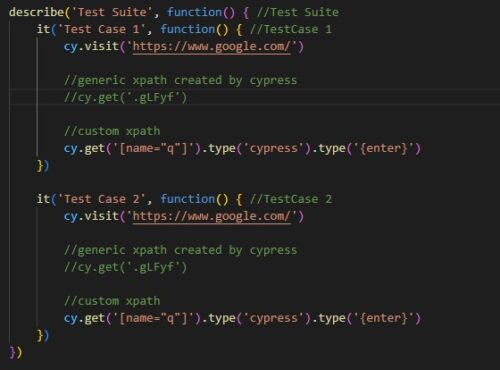
First Cypress Program:
TestCase 1 :
- Open the browser.
-
Enter text in the search box
-
Hit Enter button.
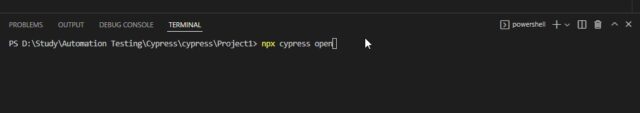
Cypress test runner:
In the ‘Terminal’ type this command – ‘npx cypress open‘
It will open the cypress GUI, and from there click on the test case which we have just created.
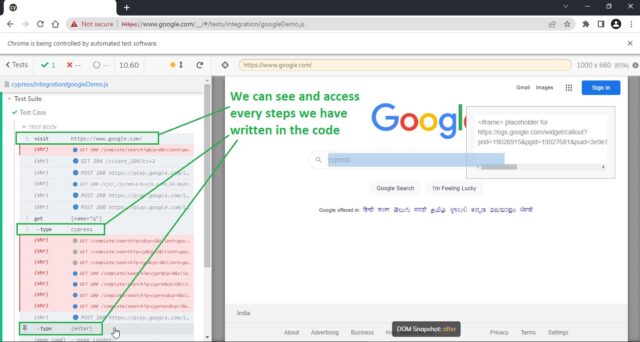
Test steps log and debugging:
We can access each steps we have written in the code by using Log and also we can iterate each step one by one by hovering them.
In a nutshell:
Cypress automation is easy to write and execute as compared to Selenium.
This blog contains only the introduction and some quick steps for getting started. I am working on another blog for detailed and step by step tutorials for Cypress automation.
See you there…



