Problem Statement:
A Banking Service loads data from different data sources into the Customer address table. When establishing data quality controls, there are bad records and duplicate records in the tables.
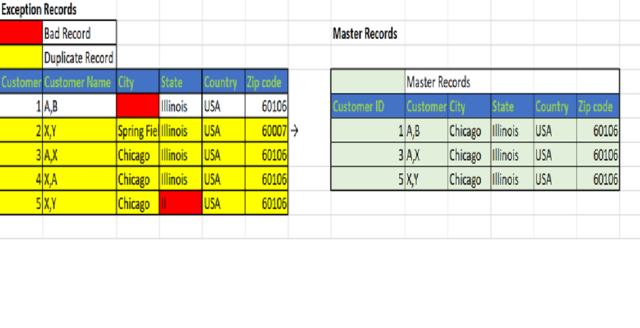
The bank wants a list of customers in Chicago, Illinois below-given table shows the example of bad records and duplicate records in the table.
Solution:
As a solution to the above problem statement, Exception Management in Informatica Data quality control can fix bad records and remove duplicate records in tables.
Process flow for Exception Management:
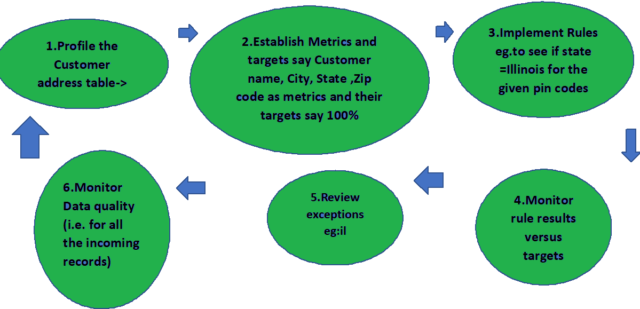
Details:
The exception records in a table generally have a match score not more than the threshold defined in the exception step to be consolidated into one record, or less than the threshold value to considered as a unique record it’s between the lower and upper thresholds, therefore, requires human analysis to make them into good and consolidated records.
Exception records are analyzed by data stewards, reviewers/Managers, changes are made and then loaded to the target table as good records in an expected format.
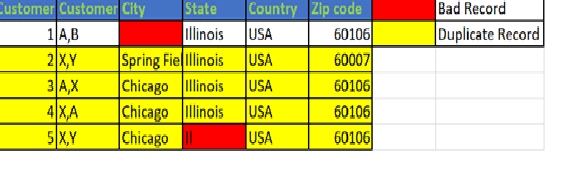
For this, a workflow with the human task is created where ->Bad records say IL in state and null in the city are fixed then-> The duplicate records are converted to consolidated records.
In exception management, exception records from the mappings move to data stewards to make changes and then to the Reviewer for approval of the changes.
To Fix bad records:
Exception management for bad records improves data accuracy,
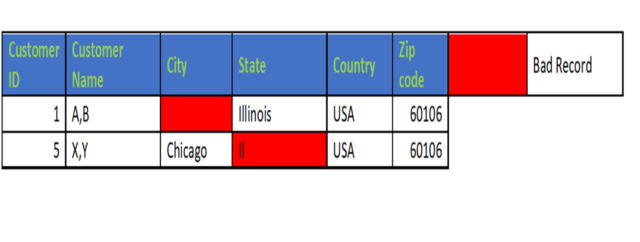
The bad records are passed as exceptions to the data steward, and they make changes in them. For example, in this state is not in the expected format here, DS corrects them manually, and the corrected records move to the reviewer for approval.
This is implemented by
Creating a workflow which contains a mapping to identify exception records followed by-> human task where exception records are sent to Data Steward and reviewer for changes (Fixed records are saved in exception table) followed by ->a mapping which is pointed to the exception table and moves the records to target table if the status of the record is approved as shown in the picture below,
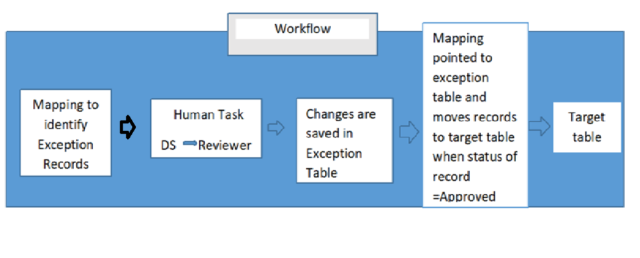
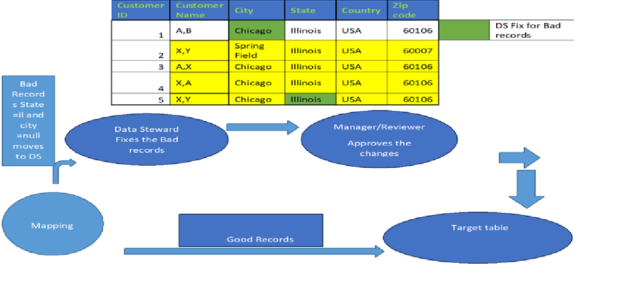
To Remove the duplicates:
The duplicate records are consolidated into one master record in the Exception Management process.
Here the duplicate records are formed as a cluster by the match transformation based on match score, and the workflow consists of cluster steps followed by human tasks.
Cluster group of duplicate records formed based on match score.
These clusters are notified to Data Steward, and they open the cluster and choose the column values to be added to the master record from the group of duplicate records as shown in pictures below,
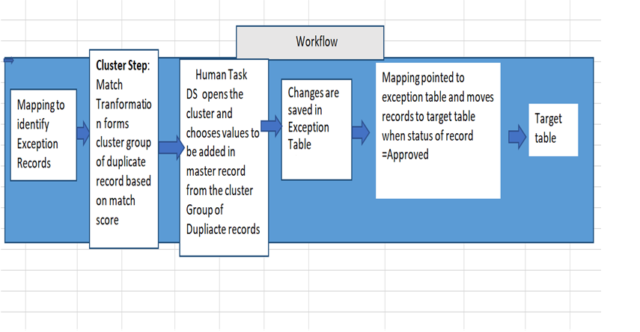
In the Example, customer name contains errors, i.e., instead of Lastname, Firstname some records its Firstname, Lastname which leads to duplicate records also few records with a different location for some person Data Steward looks into the set of duplicate records in the cluster and chooses the appropriate values to be added for the master record. And this master record is loaded to the target table with appropriate values as shown in the picture below,
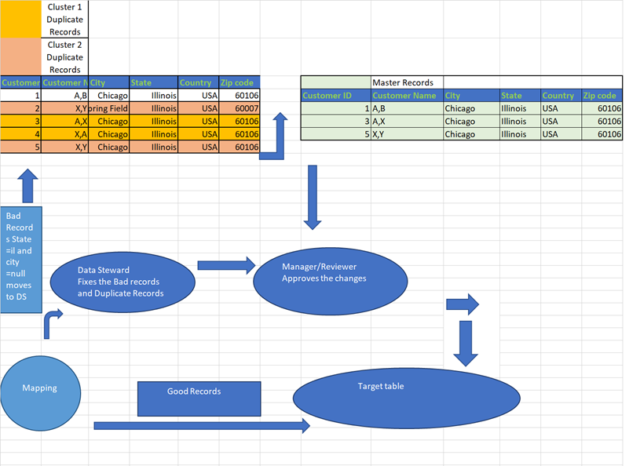
The below picture shows the Exception records, and the Master records derived post the process of Exception Management.