Out of several portal technologies and tools, Liferay, written in Java, is a free and open source enterprise software product that provides web content management and application management. As an essential component, authorization and authentication are almost always needed for each type of enterprise system tool. In the past few weeks, we completed some security configuration. It’s quite easy to configure the related parameter with Liferay’s graphic UI.
Authorization
Instead of ‘authorization’, Liferay uses the term ‘permission’ in its application and documentation. Similar to other application systems, Liferay has been implementing the role based security control mode in portlets, pages, and applications.
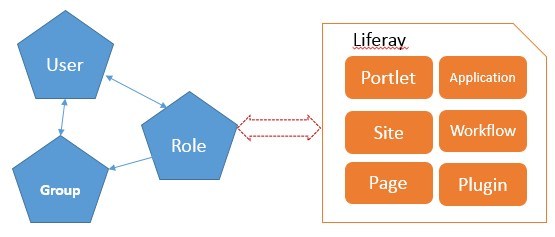
In this model, there are associations and assignments setup between objects:
- User is associated with a group;
- Group is associated with a role;
- Role is directly assigned to the permission of objects such as portlet, application, site, and pages etc;
As a result, the user or group is indirectly assigned to the Liferay objects permission. The following is an example of the permission setting on web content. Role_C is an admin and granted all permissions.
| Role | Add Discussion | Delete | Delete Discussion | Expire | Permissions | Update | Update Discussion | View |
| Role_A | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Role_B | X | |||||||
| Role_C | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
To achieve the expected security control in your organization, you will need a logical model to plan out each level and type of security. For example: who can view/edit which objects and content. With this logical mapping, you can easily implement it in the Liferay portal.
Authentication
Authentication is another pillar in the security setting. Liferay supports integration with existing security tools such as LDAP, AD, CAS, Facebook, NTLM, OpenID, Open SSO and SiteMinder. We just finished the Liferay integration with CAS which is an enterprise single sign-on service for the Web (quoted from https://www.apereo.org/projects/cas):
- An open and well-documented protocol
- An open-source Java server component
- A library of clients for Java, .Net, PHP, Perl, Apache, uPortal, and others
In this example, we will configure CAS and Active Directory in two parts. The steps are the followings:
- Go to Liferay Control Panel -> Configuration -> Portal Settings -> Authentication
- Go to CAS tab and configure as below
| Configuration | |
| Enabled | Checked |
| Import from LDAP | Checked |
| Login URL | http://gdccas |
| Logout URL | http://gdccas |
| Server Name | localhost:8080 |
| Server URL | http://gdccas |
| No Such User Redirect URL | localhost:8080 |
- Go to LDAP tab, create a new LDAP server and configure as below
| Configuration | |
| Enabled | Checked |
| Required | Checked |
| Server Name | Perficient LDAP |
| Base Provider URL | *.*.*.*:389 |
| Bsae DN | OU=Employees,DC=your company,DC=com |
| Principle | CN=you user name,OU=Employees,DC=your company,DC=com |
| Credentials | your password |
- Configure user search filter, you can refer to AD filter format
- Save your configuration
Now you can reboot the application server and access your home page. It will direct you to a CAS page and it will load all LDAP users into the Liferay user repository during startup to keep Liferay users synchronized from LDAP server.
