Why Do We Need to Secure Our Applications?
Cloud environments are very dynamic and interconnected. A single misconfiguration or exposed API key can lead to:
- Data breaches
- Compliance violations
- Costly downtime
Attackers often target application-level weaknesses, not just infrastructure gaps. If any application handles sensitive data, financial transactions, or user credentials, security is critical.
Common Mistakes Made When Building Applications
- Hardcoding API keys and credentials
- Ignoring dependency vulnerabilities
- Skipping encryption/decryption for sensitive data
Essential Security Best Practices
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
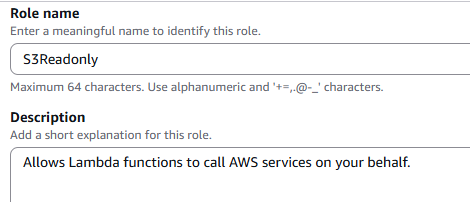
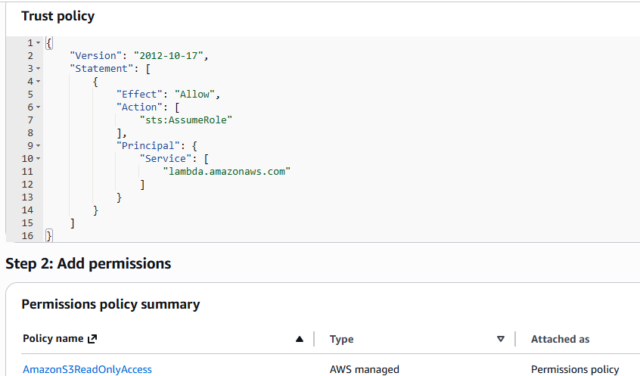
- Create dedicated IAM roles for your Lambda functions, EC2 instances, or ECS tasks instead of hardcoding access keys in your application.
- We must regularly review who has permissions using the IAM Access Analyzer.
- We must avoid using the root account for day-to-day operations/ any operations as a developer.
2. Don’t Store/Share Secrets in Your Code
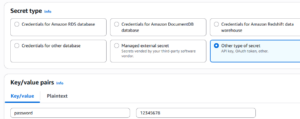
Your appsettings.json is not the right place for secret keys. Storing API keys or database passwords.
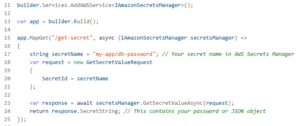
- We must use AWS Secrets Manager or Parameter Store to keep secrets safe.
- Fetch keys at runtime by using AWS SDK for .NET or the AWSSDK.Extensions.NETCore.Setup configuration provider
3. Always Encrypt Data
Encryption is one of the best practices to encrypt our sensitive data
- Enable HTTPS by default for all your endpoints.
- Use AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) to issue and manage SSL/TLS certificates.
- In your application, make sure that all traffic is redirected to HTTPS by adding app.UseHttpsRedirection();
- AWS KMS to encrypt your S3 buckets, RDS databases, and EBS volumes.
- If you’re using SQL Server on RDS, enable Transparent Data Encryption (TDE).
Encrypt & Decrypt API Key with KMS
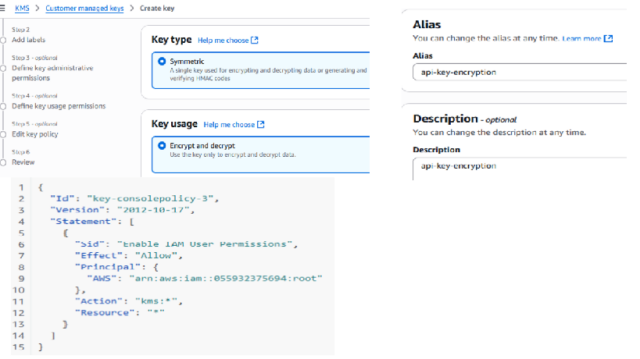

4. Build a Secure Network Foundation
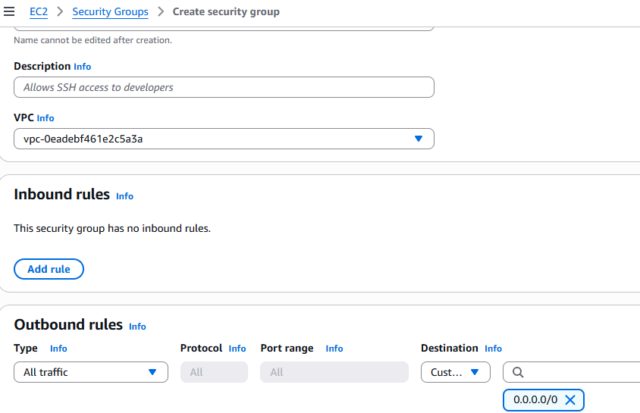
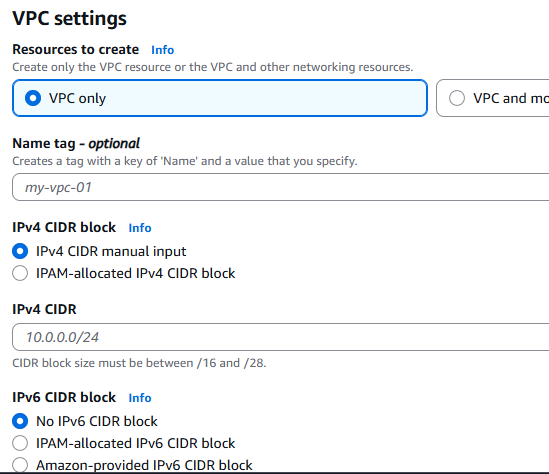
- Must use VPCs with private subnets for backend services.
- Control the traffic with Security Groups and Network ACLs.
- Use VPC Endpoints to keep traffic within AWS’s private network
- Use AWS WAF to protect your APIs, and enable AWS Shield to guard against DDoS attacks.
5. Keep Your Code and Dependencies Clean
Even the best infrastructure can’t save a vulnerable codebase.
- Update your .NET SDK and NuGet packages regularly.
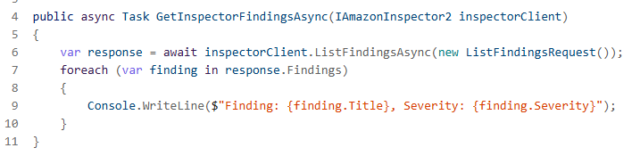
- Use Amazon Inspector for runtime and AWS environment security, and tools like Dependabot for Development-time dependency security to find vulnerabilities early.
- Add code review analysis tools (like SonarQube) in your CI/CD pipeline.
6. Log Everything and Watch
- Enable Amazon AWS CloudWatch for all central logging and use AWS X-Ray to trace requests through the application.
- Turn on CloudTrail to track every API call across your account.
- Enable GuardDuty for continuous threat detection.

