In today’s web landscape, users expect instant feedback-whether it’s receiving a new chat message, seeing a real-time stock price update, or getting notified when someone comments on a post. This shift has made real-time communication essential for modern applications.
In this beginner-friendly tutorial, we’ll explore how to build real-time features in a Next.js app using Socket.IO. You’ll understand the fundamentals, build a simple real-time chat, and learn how to integrate Socket.IO cleanly into a Next.js environment.
What Is Socket.IO?
Socket.IO is a JavaScript library that facilitates real-time, bi-directional communication between web clients and servers. It uses WebSockets under the hood but adds many improvements:
- Fallback mechanisms: Works even when WebSockets aren’t supported (e.g., via long-polling)
- Event-based communication model
- Automatic reconnection
- Broadcasting support
This makes it ideal for applications like:
- Chat systems
- Live notifications
- Multiplayer games
- Online collaboration tools
- Real-time analytics dashboards
Why Use Socket.IO with Next.js?
Next.js, as a full-stack React framework, offers static and server-side rendering, routing, API routes, and more. But real-time communication isn’t built-in. That’s where Socket.IO fits perfectly.
Benefits of using Socket.IO with Next.js:
- Easily integrates with custom Express servers
- Allows you to build both the frontend and backend in one unified project
- Provides a seamless developer experience with React
Project Setup: A Real-Time Chat App
Let’s build a basic chat app to demonstrate real-time messaging
Step 1: Create a New Next.js App
Let’s start with a fresh project. Open your terminal and run:
npx create-next-app@latest nextjs-socketio-chat cd nextjs-socketio-chat
Step 2: Install Required Packages
We need socket.io for the server and socket.io-client for the frontend. We’ll also use Express to create a custom server:
npm install express socket.io socket.io-client
Step 3: Setup a Custom Express Server
Next.js supports custom servers for extending its capabilities. Here’s how to create one with Express and integrate Socket.IO.
Create a file called server.js:
const express = require('express');
const next = require('next');
const { createServer } = require('http');
const { Server } = require('socket.io');
const dev = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production';
const app = next({ dev });
const handle = app.getRequestHandler();
app.prepare().then(() => {
const expressApp = express();
const server = createServer(expressApp);
const io = new Server(server);
// Real-time communication logic
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
console.log('A user connected:', socket.id);
socket.on('chat-message', (msg) => {
io.emit('chat-message', msg); // broadcast to all clients including sender (if you want to broadcast to all client excluding sender, you have to call socket.emit function instead of io.emit function)
});
socket.on('disconnect', () => {
console.log('User disconnected:', socket.id);
});
});
expressApp.all('*', (req, res) => handle(req, res));
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('> Server running on http://localhost:3000');
});
});
Step 4: Modify package.json Scripts
Update your package.json to use your custom server:
"scripts": {
"dev": "node server.js", …
}
Run the development server:
npm run dev
Step 5: Build the Frontend Chat Component
Create a file: src/components/Chat.tsx
"use client";
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { io } from "socket.io-client";
const socket = io();
export default function Chat() {
const [message, setMessage] = useState("");
const [chatLog, setChatLog] = useState< {
message: string;
timeStamp: number
}[]
>([]);
useEffect(() => {
socket.on("chat-message", (messages) => {
setChatLog((prev) => [...prev, messages]);
});
return () => {
socket.off("chat-message");
};
}, []);
const handleSend = () => {
if (message.trim().length > 0) {
const timeStamp = Date.now();
socket.emit("chat-message", { message, timeStamp }); // you can add username or token also with this object after adding authentication flow
setMessage("");
} else {
alert("Please enter message");
}
};
return (
<div style={{ padding: "20px", maxWidth: "600px", margin: "auto" }}>
<h2>Real-Time Chat</h2>
<div style={{ display: "flex", gap: "10px" }}>
<input
value={message}
onChange={(e) => setMessage(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Type your message"
style={{
flex: 1,
padding: "10px",
border: "1px solid #ccc",
borderRadius: 5,
}}
/>
<button onClick={handleSend}>Send</button>
</div>
<ul style={{ marginTop: "20px", listStyle: "none" }}>
{chatLog.map((chat, i) => (
<li
key={i}
style={{
padding: 10,
border: "1px solid #ccc",
borderRadius: 5,
marginTop: 15,
}}
>
{chat.message}
<span style={{ display: "block", fontSize: 12, color: "#ccc" }}>- {new Date(chat.timeStamp).toLocaleString()}</span>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
Step 6: Load the Chat Component in a Page
Update src/app/page.tsx:
import Chat from "@/components/Chat";
export default function Home() {
return (
<div>
<Chat />
</div>
);
}
Step 7: Test the Application
Start the server:
npm run dev
Open http://localhost:3000 in two tabs or two different browsers.
Send a message in one tab and it will instantly appear in the other.
Output:
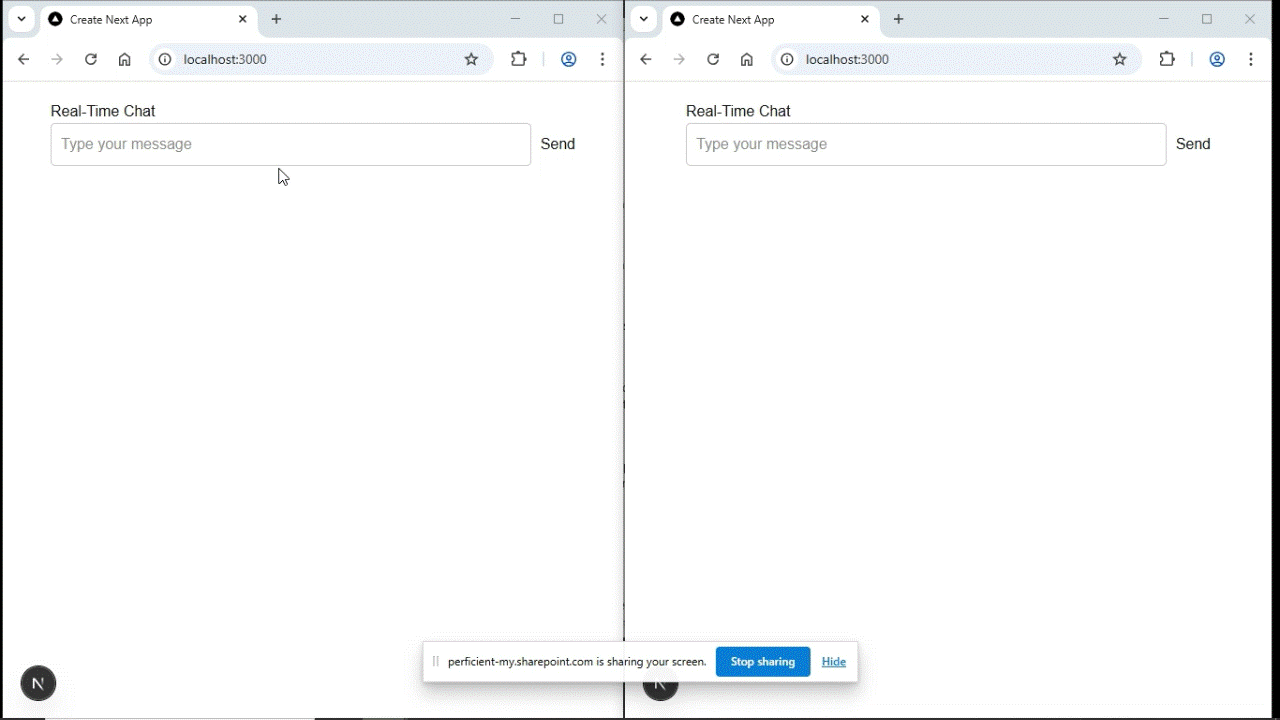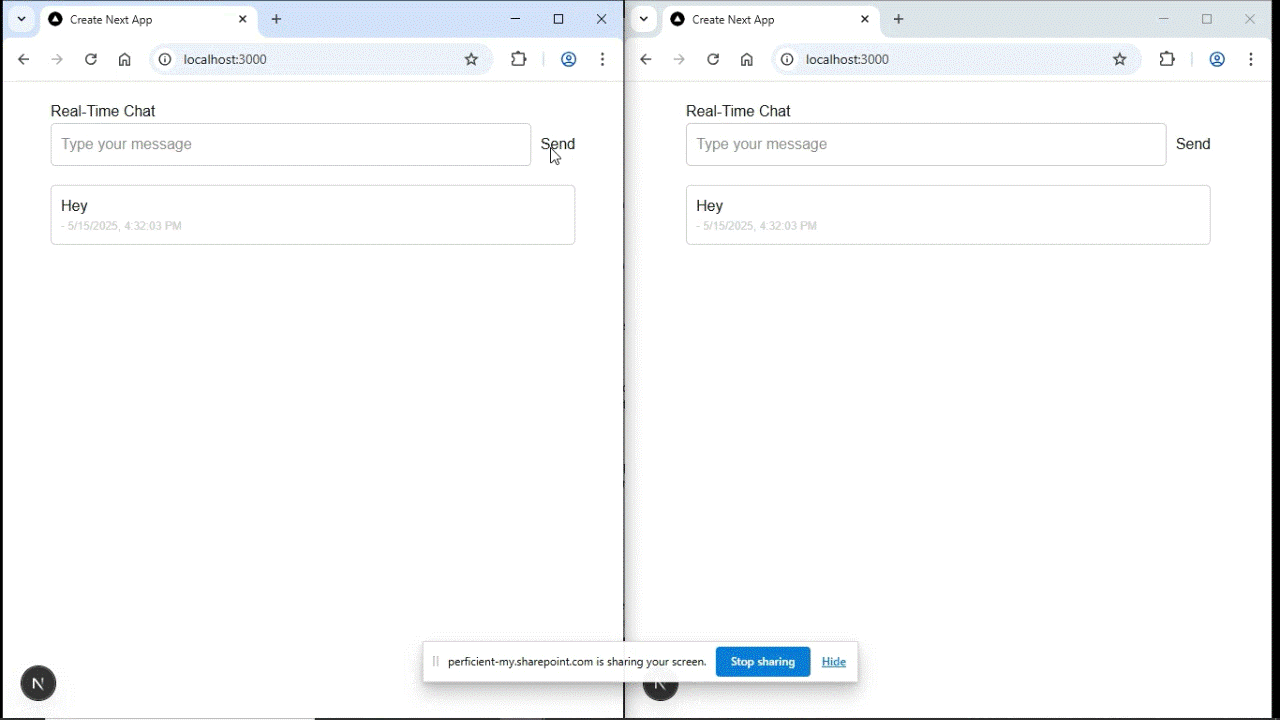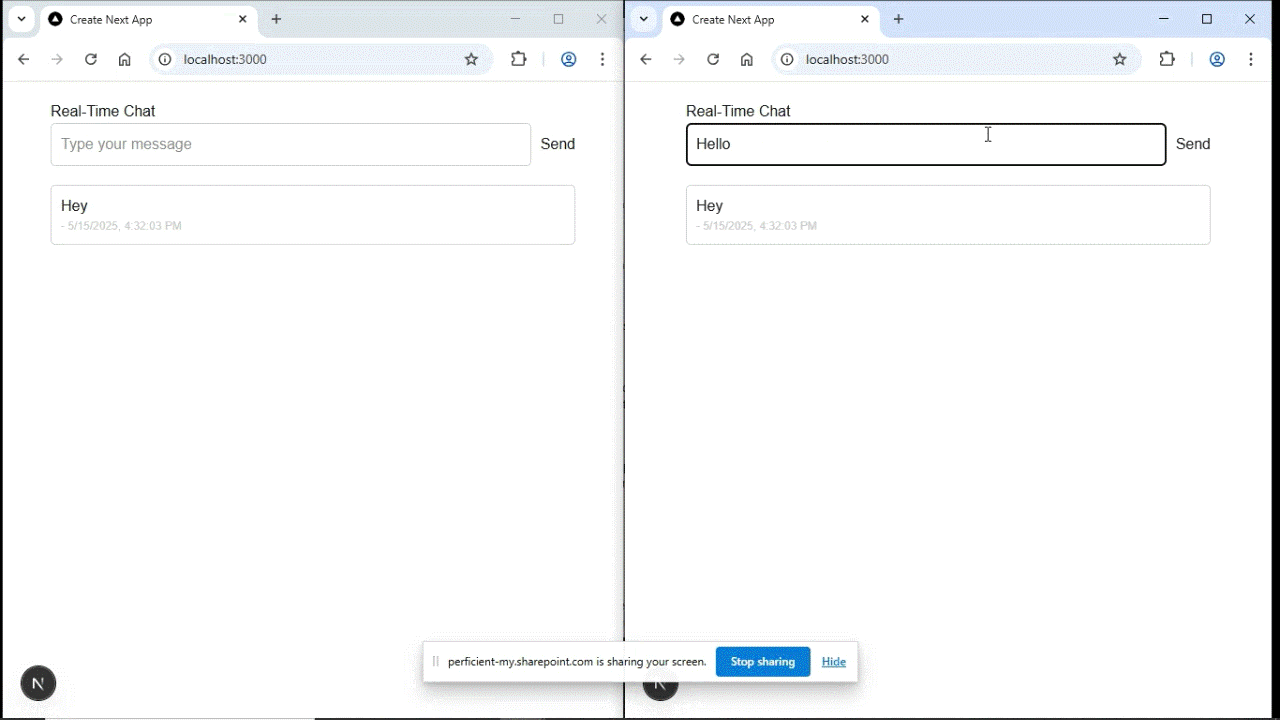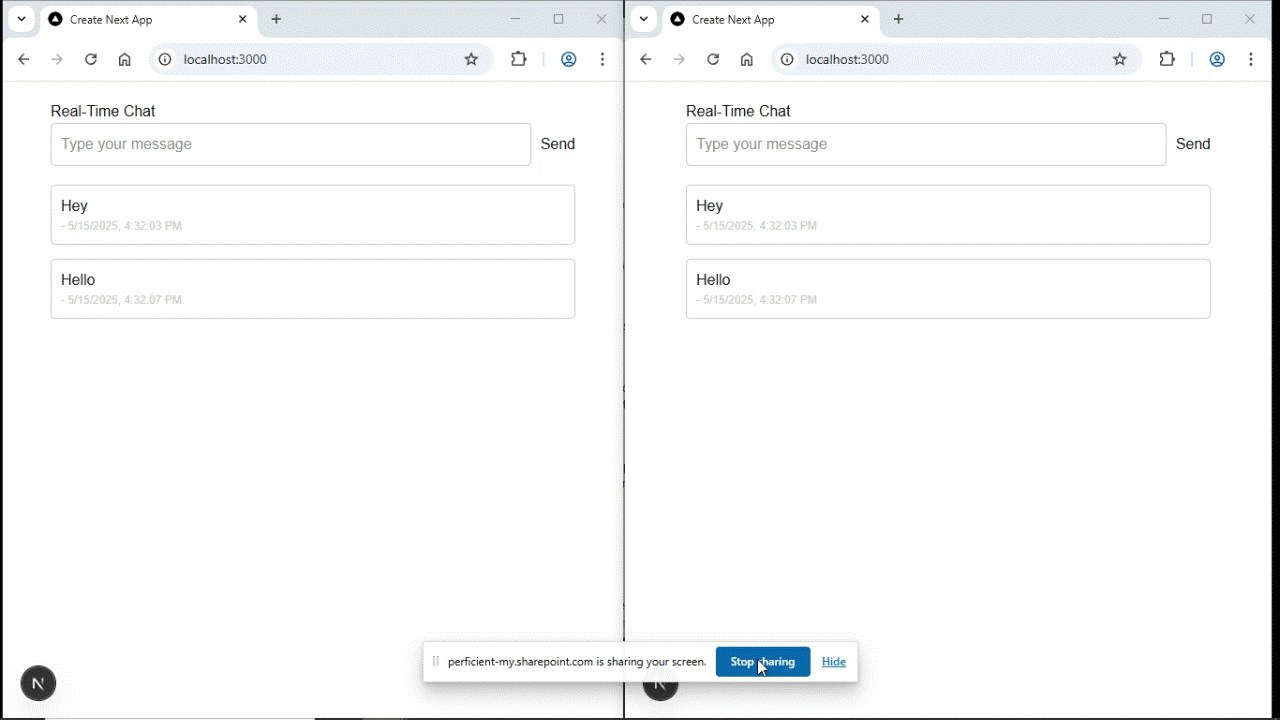
Congratulations! You now have a working real-time chat app using Socket.IO and Next.js.
How Socket.IO Works Under the Hood
Socket.IO uses a publish/subscribe (pub-sub) pattern. Events like ‘chat-message’ act as channels that clients and servers subscribe to or emit.
Key Concepts:
- Socket: A persistent connection between the client and server
- Events: Custom named messages exchanged (chat-message, user-joined)
- Broadcasting: Send data to multiple clients at once
Unlike HTTP requests which are client-initiated, sockets keep the connection open both ways.
Advanced Socket.IO Features to Explore Later
- Rooms: Group sockets together to send targeted messages
- Namespaces: Create separate channels for different purposes
- Middleware: Add authentication before accepting socket connections
- Scaling: Use Redis adapter to scale Socket.IO across multiple servers
Common Use Cases in Next.js Projects
- Chat Applications: Support group or private messaging
- Live Notifications: Show instant updates like “New order placed”
- Collaborative Tools: Real-time whiteboards or documents
- Live Dashboards: Auto-updating sales, user, or stock data
- Gaming: Multiplayer games using sockets for live sync
Conclusion
Adding real-time features like chat, notifications, or live dashboards is easy and efficient when using Socket.IO with Next.js. With a custom server, dynamic client components, and event-driven messaging, you’re equipped to build responsive and interactive apps that users love.
Socket.IO’s ease of use, power, and flexibility make it a go-to solution for real-time web communication.

