As Salesforce developers, handling JSON responses is a common task when working with external APIs or manipulating data structures. Apex provides several powerful methods to deserialize JSON into native objects, making it easier to work with structured data. In this blog, we will explore different approaches to deserialize JSON in Apex, accompanied by examples for better understanding.
1.Using JSON.deserialize() Method
This method is straightforward and deserializes JSON content into an Object. The returned object can be cast to a specific type for further processing.
Example:
String jsonString = '{"name": "John Doe", "age": 30}';
Object obj = JSON.deserialize(jsonString, Object.class);
Map<String, Object> mapData = (Map<String, Object>) obj;
System.debug('Name: ' + mapData.get('name'));
System.debug('Age: ' + mapData.get('age'));
When to Use:
- When the JSON structure is simple.
- If the JSON structure can vary and type casting is manageable.
2.Using JSON.deserializeUntyped() Method
This method deserializes JSON into loosely typed objects such as Map<String, Object> or List<Object>. It is useful when you need flexibility without creating a custom class.
Example:
String jsonString = '{"name": "Jane Doe", "hobbies": ["reading", "traveling"]}';
Map<String, Object> data = (Map<String, Object>) JSON.deserializeUntyped(jsonString);
System.debug('Name: ' + data.get('name'));
List<Object> hobbies = (List<Object>) data.get('hobbies');
System.debug('Hobbies: ' + hobbies);
When to Use:
- For dynamic or unpredictable JSON structures.
- When a custom class is unnecessary.
3. Using JSON.deserializeStrict() Method
This method is similar to JSON.deserialize() but enforces strict type matching between the JSON string and the target Apex type. It throws an exception if the types do not match.
Example:
String jsonString = '{"name": "Mark", "age": 25}';
try {
Map<String, Object> mapData = (Map<String, Object>) JSON.deserializeStrict(jsonString, Map<String, Object>.class);
System.debug('Name: ' + mapData.get('name'));
System.debug('Age: ' + mapData.get('age'));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.debug('Error: ' + e.getMessage());
}
When to Use:
- When you need to enforce data integrity during deserialization.
- For scenarios where strict type validation is critical.
4. Using Custom Apex Classes
Defining a custom class that maps to the JSON structure is a robust approach. This method is ideal for complex and nested JSON objects.
Example:
public class Person {
public String name;
public Integer age;
}
String jsonString = '{"name": "Alice", "age": 28}';
Person person = (Person) JSON.deserialize(jsonString, Person.class);
System.debug('Name: ' + person.name);
System.debug('Age: ' + person.age);
When to Use:
- For well-defined and static JSON structures.
- When reusability and readability are priorities.
5. Handling Nested JSON with Custom Classes
For nested JSON structures, create multiple classes to mirror the JSON hierarchy.
Example:
public class Order {
public String orderId;
public List<Item> items;
}
public class Item {
public String itemName;
public Double price;
}
String jsonString = '{"orderId": "ORD123", "items": [{"itemName": "Laptop", "price": 1200.50}, {"itemName": "Mouse", "price": 25.75}]}';
Order order = (Order) JSON.deserialize(jsonString, Order.class);
System.debug('Order ID: ' + order.orderId);
for (Item item : order.items) {
System.debug('Item: ' + item.itemName + ', Price: ' + item.price);
}
When to Use:
- For deeply nested or complex JSON structures.
- When maintaining clear relationships between objects is essential.
6. Deserializing JSON Arrays
If the JSON is an array, you can deserialize it directly into a List of objects or a List of custom classes.
Example:
String jsonString = '[{"name": "John"}, {"name": "Jane"}]';
List<Person> people = (List<Person>) JSON.deserialize(jsonString, List<Person>.class);
for (Person person : people) {
System.debug('Name: ' + person.name);
}
When to Use:
- When the JSON represents an array.
- For scenarios requiring bulk processing.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct method to deserialize JSON in Apex depends on the complexity of the JSON structure and your application’s requirements. Here’s a quick summary:
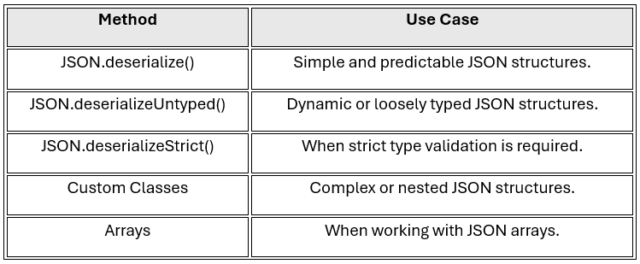
Understanding these approaches enables you to efficiently handle JSON in your Salesforce applications and create robust, maintainable solutions. Happy coding!

