In this blog post, I will guide you through the process of implementing a Spring Expression Language (SpEL) validator in a Spring Boot application. SpEL is a powerful expression language that supports querying and manipulating an object graph at runtime. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a working example of using SpEL for validation in your Spring Boot application.
Project Structure
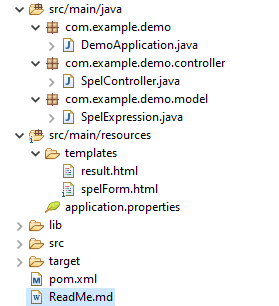
Step 1: Set Up Your Spring Boot Project
First things first, let’s set up your Spring Boot project. Head over to Spring Initializer and create a new project with the following dependencies:
- Spring Boot Starter Web
- Thymeleaf (for the form interface)
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <version>3.4.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> <version>3.4.2</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
Step 2: Create the Main Application Class
Next, we will create the main application class to bootstrap our Spring Boot application.
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
Step 3: Create a Model Class
Create a SpelExpression class to hold the user input.
package com.example.demo.model;
public class SpelExpression {
private String expression;
// Getters and Setters
public String getExpression() {
return expression;
}
public void setExpression(String expression) {
this.expression = expression;
}
}
Step 4: Create a Controller
Create a controller to handle user input and validate the SpEL expression.
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.model.SpelExpression;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.SpelParseException;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
@Controller
public class SpelController {
private final ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
@GetMapping("/spelForm")
public String showForm(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("spelExpression", new SpelExpression());
return "spelForm";
}
@PostMapping("/validateSpel")
public String validateSpel(@ModelAttribute SpelExpression spelExpression, Model model) {
try {
parser.parseExpression(spelExpression.getExpression());
model.addAttribute("message", "The expression is valid.");
} catch (SpelParseException e) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Invalid expression: " + e.getMessage());
}
return "result";
}
}
Step 5: Create Thymeleaf Templates
Create Thymeleaf templates for the form and the result page.
spelForm.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>SpEL Form</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f4f4f9;
color: #333;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
.container {
background-color: #fff;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
text-align: center;
}
h1 {
color: #4CAF50;
}
form {
margin-top: 20px;
}
label {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 8px;
font-weight: bold;
}
input[type="text"] {
width: 100%;
padding: 8px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
button {
padding: 10px 20px;
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: #fff;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>SpEL Expression Validator</h1>
<form th:action="@{/validateSpel}" th:object="${spelExpression}" method="post">
<div>
<label>Expression:</label>
<input type="text" th:field="*{expression}" />
</div>
<div>
<button type="submit">Validate</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
result.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Validation Result</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f4f4f9;
color: #333;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
.container {
background-color: #fff;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
text-align: center;
}
h1 {
color: #4CAF50;
}
p {
font-size: 18px;
}
a {
display: inline-block;
margin-top: 20px;
padding: 10px 20px;
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: #fff;
text-decoration: none;
border-radius: 4px;
}
a:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Validation Result</h1>
<p th:text="${message}"></p>
<a href="/spelForm">Back to Form</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Step 6: Run the Application
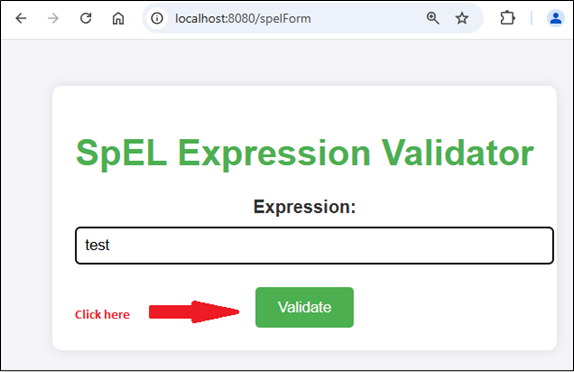
Now, it’s time to run your Spring Boot application. To test the SpEL validator, navigate to http://localhost:8080/spelForm in your browser.
For Valid Expression
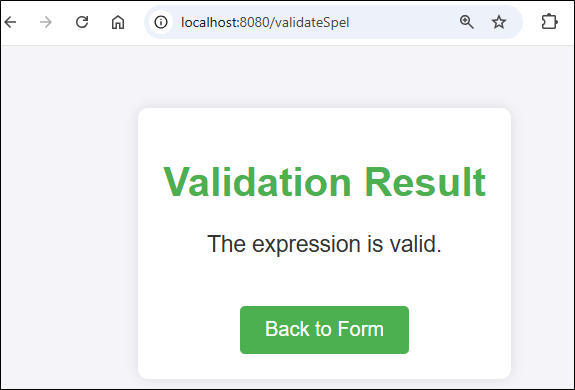
For Invalid Expression
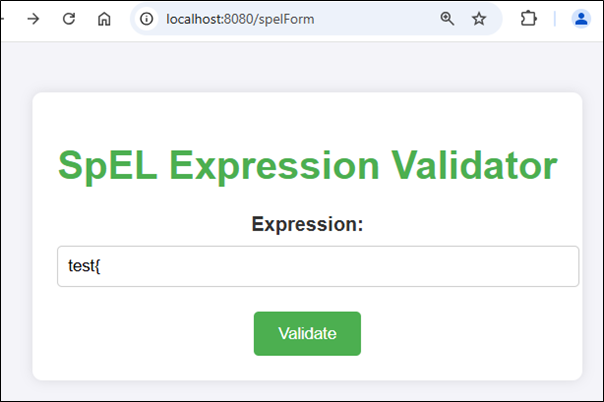
Conclusion
Following this guide, you successfully implemented a SpEL validator in your Spring Boot application. This powerful feature enhances your application’s flexibility and robustness. Keep exploring SpEL for more dynamic and sophisticated solutions. Happy coding!

