In this tutorial, we’ll explore how to achieve Vue.js Location Autocomplete by integrating the Google Maps Places Autocomplete API with a custom Geo Location component. We’ll walk you through each step to set up the Vue.js Location Autocomplete feature, manage user input, and bind it to Vue’s v-model for smooth two-way data binding.
Prerequisites for Vue.js Location Autocomplete
To start with Vue.js Location Autocomplete, ensure you have a basic understanding of Vue.js and TypeScript. Additionally, you need to enable the Maps API on your Google Cloud account.
Steps to Build a Google Maps Autocomplete Component
Step 1: Set Up the Google Places API
First, activate the Places API through the Google Cloud Console and obtain your API key. Subsequently, load the Google Maps script in your application, typically in your index.html file. For more details, refer to the Google Maps Places API documentation.
![]()
![]()
Step 2: Set Up the Basic Component
Next, create a Vue component called Geo Location. This component will use Google Maps’ Places Autocomplete service to fetch location data. For more information on Vue.js, visit the Vue.js documentation.
Here’s the component template:

This Vue.js template defines an input field for integrating the Google Maps Places Autocomplete API:
<input type="search">: Defines a search box for location input.ref="textbox": Allows direct access to the input element in the script.:placeholder="'search location'": Binds the placeholder to a static string.:value="value": Binds the input value to a reactive value property.@input="input": Calls the input method when the user types in the field.@change="change": Calls the change method when the input value changes.
Step 3: Define the Component in TypeScript
Then, Set up the structure for your Geo Location component using TypeScript, and use vue-property-decorator to manage props and Vue lifecycle hooks.
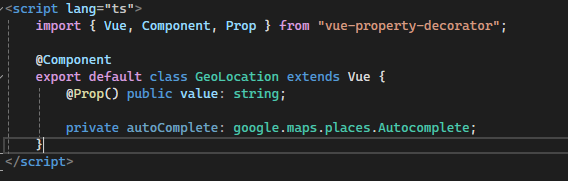
- Use the
@Componentdecorator from vue-property-decorator to define the Geo Location component. - Use the
@Prop()decorator to pass the value prop from the parent component. - Consequently, the value prop is bound to the v-model.
Step 4: Access the Input Element
To work with Google Places Autocomplete, reference the input element with a getter:
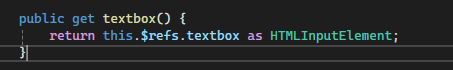
- Retrieve the input element using
this.$refs.textboxand therefattribute from the template. - Furthermore, ensure TypeScript recognizes the element as an HTMLInputElement by using it as
HTMLInputElement, providing proper type safety.
Step 5: Initialize Google Places Autocomplete
Inside the mounted lifecycle hook, initialize the Google Places Autocomplete object and bind it to your input field. Also, listen for the place_changed event to capture when a place is selected from the dropdown. For additional information, see the Google Maps JavaScript API documentation.
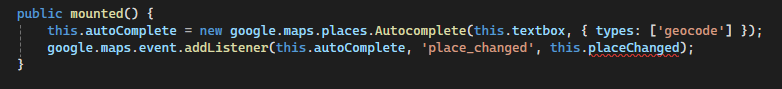
- Create an instance of Google’s Autocomplete for the input field, thereby enabling suggestions for location searches.
- Moreover, a listener can be added to detect when a user selects a place from the suggestions. As a result, call the placeChanged method to handle the selected place.
Step 6: Handle Input and Change Events
Define methods to handle user input and change events.
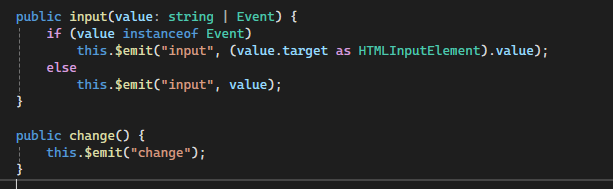
- The
inputmethod triggers whenever the user types in the input field. - Similarly, the
changemethod fires when a selection is made.
Step 7: Capture Selected Place
The placeChanged method triggers when the user selects a location from the dropdown. Here, extract either the formatted_address or the place’s name and pass it to the parent component.
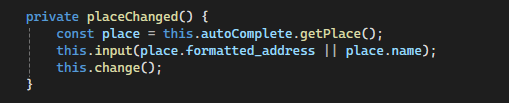
- Retrieve the selected place from the Autocomplete suggestions using
this.autoComplete.getPlace(). - Consequently, emit the selected place’s
formatted_addressor name back to the parent component via theinput()andchange()methods.
Step 8: Use in Parent Component
Finally, use the GeoLocation component in a parent component as shown below:

- Bind the input value to the
selectedLocationdata property using thev-modeldirective. - In addition, dynamically apply the ‘has-error’ class if the location search fails using
v-bind: class.
By following this approach, you can easily integrate Google Maps Places Autocomplete into your Vue.js applications, thereby enhancing the user experience when entering location data. This guide provides a flexible and reusable way to work with location-based inputs.

