One of the most widely used website development platforms in the world is the open source Drupal content management system (CMS). Drupal allows for easy creation and maintenance of any website, thanks to its numerous features, capabilities, and advantages. Drupal appeals to a wide range of stakeholders as it also makes it simple to distribute information to various channels that are crucial for today’s businesses:
- Developers place high value on Drupal due to its open-source adaptability, stability, security, and robust contributing community.
- Marketers highly regard Drupal for its intuitive interface, contemporary content authoring capabilities, and seamless compatibility with their preferred marketing technology solutions.
- Business leaders recognize Drupal’s capacity to foster corporate agility, innovation, and competitiveness.
Discover what’s new in Drupal 11.0 compared to its Drupal 10.0:
- Single Directory Components (SDC): UI component creation now standardized through SDC.
- Recipes: A feature that facilitates the integration of new features by utilizing predefined configurations.
- Optimized Page Performance: Improved speed of interface previews and lazy loading for enhanced performance.
- Content Modeling: The process of reusing existing fields and creating new ones has been simplified.
- Enhanced Decoupled Menu Support: Improved support for decoupled menus, including Link-set support.
- Simplified Management: Menu, taxonomy, and permission management made easier.
- Symfony 7 Integration: Upgraded to Symfony 7, replacing Symfony 6.
- Streamlined Content Editing: Content editing made more efficient with automatic formatting.
- Improved Administration Back End: Enhanced features in the administration back end, alongside other enhancements.
Explore the Key Improvements and Enhancements in Drupal 11.0
Enhanced Administrative Interface
Site admins may now make use of several useful new capabilities. To begin with, the traditional administrative toolbar loads quicker on both front-end and back-end sites, allowing you to work on your critical responsibilities more quickly. Additionally, you may now build pages in Views that, independent of their route, display in the administrative theme thanks to a new option.
Permissions are a common tool used by site administrators. A simple filter was introduced to make it easier to manage permissions and locate the appropriate permissions for the work at hand. Additionally, a new Announcements Feed module was included by default to new Drupal installations to assist in informing site administrators of current events. To keep site owners and administrators updated on project news, the Announce module offers a feed of announcements from the Drupal Association and the Drupal project within Drupal core.
Additionally, Drupal features a brand-new experimental Navigation module that completely revamped the traditional toolbar. The vertical sidebar collapses to the left, making it easier to navigate the administrative menu. It is also quite configurable; you can add additional menu blocks and modify the pre-installed ones.
Isolated Workspaces: Previewing Content Changes Before Publication
The Workspaces module in Drupal has been stabilized, enabling users to simultaneously plan and stage content changes. Content owners can work on alternative content updates, such when results from athletic events are made accessible or when releasing new material necessitates updating several pages of the website simultaneously, requiring advance content approval.
Experience Improved Taxonomy Capabilities
Taxonomy now provides a visual UI that can be used to view, revert, and delete revisions. It is also now possible to apply a content moderation workflow to taxonomy terms.
Streamlined Decoupled Navigation
Drupal is already a fantastic CMS for front-end JavaScript apps because of its simple to build up API mechanism. Nevertheless, controlling the navigation proved difficult and frequently aggravating. The addition of specialized endpoints that make use of the Linkset standard has helped to overcome this issue by making it easier to navigate between content parts in decoupled contexts. Instead of hard-coding navigation, a front-end developer may now easily render it by consuming menu data. It also implies that managing application menus may be done without writing code by non-developers.
Simplified Menu Creation Process
Additionally, the capability to construct menus has been enhanced. Editing menu items and directly adding child menu items is simpler.
Experience the Freedom of Flexible Block Management
In the administrative interface, custom blocks may be easily created by site builders under Structure. You can manage blocks according to type and reverse back any changes made to block content if necessary, with more specific permissions. Block management includes the ability to display or conceal blocks on pages according to response statuses (such as “success,” “access denied,” or “not found”).
File and Media Management is Now More Efficient and User-Friendly
Filename sanitization and transliteration options are available right out of the box for file uploads in modern Drupal. Among other things, this offers choices for lowercasing and replacing whitespace. Revision editing for media entities is now supported, and WebP is now used by Drupal core’s default image styles to minimize image sizes by about 25%–34%.
Create efficient UI components with Single-Directory Components (SDCs)
The Single-Directory Components module, which was first developed at https://www.drupal.org/project/sdc, is now stable and a part of Drupal core. When all necessary elements are in one place, components are simpler to build, easier to locate, and can be reused across the website. SDC has proved to be a popular feature since it allows front-end developers to deal with Drupal without having to know anything about it.
Revolutionizing Site Building with Innovative Recipes APIs
Recipes offer automatic site-building phases that are combinable and leave no trace on the site after they are applied, so addressing the drawbacks of earlier Drupal install profiles and opening the door to more modular site construction.
There are a lot of real-world applications for recipes. For example, let’s imagine you wish to expedite the steps necessary to enable event signups. You might obtain the appropriate modules and set them up for that use case with the aid of a recipe. Recipes encourage composable components, minimize the amount of site construction necessary, and remove the need to download each individual module.
Install profiles are still supported by Drupal 11 and are used by default for installation; however, the built-in profiles have been divided into component recipes, which will be the way composable Drupal site construction moves forward.
Drupal 11’s Optimized Core Code Delivers Significant Performance Gains
For Drupal 11, a great deal of work went into making the foundation of the platform smaller and leaner. The code has been greatly simplified and cleaned up by contributors to highlight Drupal’s key features and benefits, such as security and performance.
Contributors have often rewritten code to make it more effective. All obsolete code has been eliminated from Drupal 10. This lessens ambiguity and duplication in Drupal’s APIs. It benefits everyone because PHP 8.3 makes running your updated apps considerably faster as well.
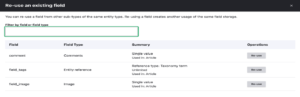
Experience Easier Content Modeling and Management
Drupal users embraced the redesign of the reusing existing fields user interface, which made it simpler to establish consistent content models. Text fields now enforce a specific text format, simplifying the content editors’ experience. Whether content is in content blocks, nodes, or other entity types, managing older versions of content is now simpler thanks to the addition of a single entity revision editing experience. A floating action bar that lets users swiftly perform activities on multiple chosen content items has also improved the functionality for bulk operation lists.
Modernizing JavaScript Development Practices
Certain jQuery UI applications have been updated with modern JavaScript components. Furthermore, developing for Drupal now requires fewer steps without the need for extra builds thanks to on-the-fly JavaScript file minification.
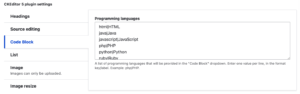
Improved Authoring and Editing in Drupal 11 with CKEditor 5
Improved “Code block” button in CKEditor settings. You may now choose the particular markup or programming language it should show. Also, Drupal’s built-in WYSIWYG editor, CKEditor 5, now has an autoformat function that detects when you are entering a a header, a list, or automatically formats it appropriately.
Experience Faster Page Loads with Enhanced Lazy Loading
Drupal reduces initial page load times by allowing web browsers to dynamically fetch extra page information after loading the first page using BigPipe. BigPipe now allows interface previews for delayed material as of Drupal 10.1. This simplifies the user experience and lessens page reflows. Additionally, starting with Drupal 10.1, it is possible to enable embedded content to load slowly so that it doesn’t slow down the first page load, as well as responsive pictures.
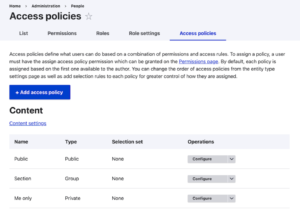
Advanced Access Policy Options
The access policy API can be used to implement access granting and checking solutions beyond permissions and user roles. It is possible to consider other circumstances and settings, such as the user’s usage of two-factor authentication or reaching an activity rate cap. The new API has replaced Drupal’s previous permissions and roles-based access management, and additional access policies can be added by custom or contributed projects.
Proactive Performance Monitoring
Gander, an automated testing framework for tracking core performance, has been incorporated into Drupal core since version 10.2. With Gander, we can keep an eye on performance over time to make sure that code changes don’t inadvertently cause performance regressions to occur again. It is now simpler to resolve problems based on such data because a dashboard for important metrics is provided.
An extension of a typical functional test, a Gander performance test gathers extra performance measurements throughout the page lifetime to provide valuable insights into critical web components. First contentful paint (FCP), Largest contentful paint (LCP), and Time to first byte (TTFB).
![]()
Furthermore, a number of additional modules that are no longer part of Drupal core are still accessible as contributed projects. Less frequently used modules, those not included in an ecosystem, and modules that weren’t expanded upon by other modules are the ones that were eliminated.
- Action UI
- Activity Tracker
- Book
- Forum
- Statistics
- Tour
What is Drupal 10’s support lifespan and upgrade timeline?
Up until the middle of 2026, when Drupal 12 is released, Drupal 10 will be maintained. This means that upgrading to Drupal 11 is not urgent. In contrast to the day of Drupal 11’s debut (August 2024), more contributed extensions could be available later.

