Welcome back to our ongoing series on assistive technologies! In our previous post, we started exploring these incredible innovations and their profound impact on the lives of individuals with disabilities. In this installment, we will continue our journey by delving into visual assistive technologies for digital accessibility. Join us as we explore the advancements in this field and how they are transforming the digital landscape to make it more inclusive for everyone.
Enhancing Digital Accessibility with Visual Assistive Technologies
Visual assistive technologies have revolutionized the way individuals with visual impairments interact with digital content, ensuring equal access to information, communication, and online experiences. These innovative tools are designed to bridge the accessibility gap and empower individuals with visual impairments to navigate and engage with digital interfaces effortlessly. Let’s explore some of the key advancements in visual assistive technologies that are making a significant impact:
Screen Readers
Screen readers are fundamental tools that convert on-screen text into synthesized speech or braille output, enabling individuals with visual impairments to “read” and comprehend digital content effectively. These software applications utilize advanced techniques such as optical character recognition (OCR) and text-to-speech synthesis to provide a comprehensive auditory or tactile representation of the information displayed on a screen. Popular screen readers like JAWS, NVDA, and VoiceOver cater to different operating systems and devices, offering seamless accessibility to a wide range of users.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)

OCR technology has opened up new possibilities for individuals with visual impairments to access printed materials. OCR software can scan documents or images and convert printed or handwritten text into machine-readable text, which can then be read aloud by a screen reader or displayed in braille using a braille display. This technology is particularly valuable for reading books, articles, documents, and even interpreting physical signs or menus. Widely used OCR tools like Tesseract, Adobe Acrobat, and ABBYY FineReader have empowered individuals to access a wealth of information that was once inaccessible.
Magnification and Contrast Adjustments

Individuals with low vision often benefit from tools that enhance the visibility of on-screen content. Magnification software allows users to zoom in on specific areas of the screen, increasing the size of text and graphics. Additionally, contrast adjustment tools enable users to modify colors and contrast levels to suit their visual needs, improving legibility and usability. ZoomText, built-in Zoom and Display Accommodations features on macOS, and similar tools have significantly enhanced the user experience for individuals with low vision.
Color Identification and Differentiation

Color blindness or color vision deficiencies can pose challenges when interpreting visual information. Visual assistive technologies provide color identification and differentiation tools to overcome these challenges. Color identification software analyzes and identifies colors on the screen, enabling users to understand visual elements effectively. Furthermore, color contrast analyzers help ensure that the color combinations used in an interface meet accessibility standards, ensuring important information is not lost due to poor color choices. Tools such as Color Oracle and Contrast Analyser have become valuable resources in ensuring inclusive color design.
Tactile Graphics and 3D Printing
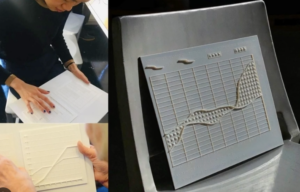
Understanding complex visual content, such as graphs, maps, or diagrams, can be challenging for individuals with visual impairments. Tactile graphics technology allows the conversion of visual information into raised tactile representations, enabling users to explore and comprehend content through touch. These tactile graphics can be produced using embossing techniques or generated with 3D printers, offering a more interactive and immersive experience. By combining tactile graphics with audio descriptions, individuals with visual impairments can gain a comprehensive understanding of visual content, fostering a truly inclusive learning and information-sharing environment.
Visual assistive technologies have revolutionized digital accessibility, empowering individuals with visual impairments to overcome barriers and actively participate in the digital world. From screen readers and OCR to magnification tools and tactile graphics, these advancements have made significant strides in creating an inclusive digital landscape. As technology continues to evolve, it is imperative for developers, designers, and content creators to prioritize accessibility, ensuring that their digital platforms are optimized for visual assistive technologies. Together, we can foster a more inclusive and equitable digital environment for individuals of all abilities.
What is next?
Remember, assistive technologies are not just tools; they are enablers of dreams and agents of change. Stay tuned for more enlightening insights!
Join us in our next post, where we will continue this enlightening journey into the realm of assistive technologies. We will uncover more types, discuss real-life success stories, and examine the future prospects for these life-changing innovations.
For more information on why accessibility is important in general, you can check out my previous blog post here.
For further information on how to make your product accessible to your audience, contact our experienced design experts, check out our Accessibility IQ for your website, download our guide Digitally Accessible Experiences: Why It Matters and How to Create Them, read more from our UX for Accessible Design series.

