Docker is an open platform that gives customers the ability to deploy multiple o/s containers on any give host. This allows for the deployment of multiple environments without having to incur the overhead of having a virtual machine for each environment. Docker uses Linux o/s facilities like namespaces, groups and union capable file systems to deploy lightweight containers.
Why we use Docker install Oracle server. Advantages:
- Use the Docker install to set up the Oracle server in several minutes by downloading the presenting Docker images file. Traditionally, it takes much more time to install step by step.
- Docker install Oracle server can easy backup the Oracle server, it just uses the Docker export command to export the current Oracle server into one Docker images file.
- Effective usage of the computer hardware server to install several Oracle version servers into one Linux server.
In this section, I will show how to use the Docker platform to install the two different Oracles versions, Oracle 11g and Oracle 12C server into one Linux server. Note: This should follow the Oracle software license agreement, it should not be used for commercial purposes.
The following steps will instruct you on how to install the Docker container for Oracle 11g and Oracle 12c.
- Install Docker
Docker is free software and can be downloaded from the website via their website. In our case, we installed Docker in the Linux. Prior to installation, check the Linux version of Ubuntu. It should be 64 bit and the version should later than 3.10.
Use the below command to check the Ubuntu version:
- Start Oracle 11g and Oracle 12 C Container
It has free Docker Oracle images presented.You can use the below command to pull the Oracle Docker image files into the Docker container. Of course, you can write your own Docker file to facilitate it.
1.Run the below command in Linux. It pulls the Oracle 12 c Docker image files into Ubuntu.
2.Run the below command in Linux. It will pull the Oracle 11 g Docker image file into Ubuntu.
3.Run the below command to check the pulled Docker images.
4.Run the below command to create and start the Docker container of Oracle 11g with port 1521
5.Run the below command to create and start the Docker container of Oracle 12c with port 1522.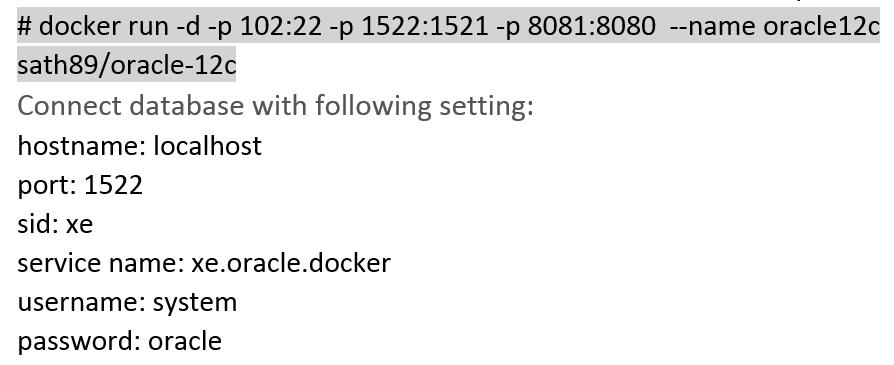
6.Use the following command to stop the Oracle server.
7.Create your Oracle Docker image. It is also the way to back up your Oracle server.
- Set Oracle Server after installation
Once the container has been started and the databases 11g and 12c are created, you can connect to it just like to any other database:
Oracle 11g uses port 1521 and Oracle 12c uses port 1522. Use sqlplus to connect to oracle with a different user ID.
There are two ports that are exposed in this image:
- 1521, which is the port to connect to the Oracle Database.
- 8080, which is the port of Oracle Application Express (APEX).
The Oracle Database inside the container also has Oracle Enterprise Manager Express configured. To access OEM Express, start your browser and follow the URL:
https://localhost:8080/em/ — oracle 11g
https://localhost:8080/em/ — oracle 12c






