Objective
Enable automated document summarization by allowing us to upload TXT, PDF, or DOCX files, extracting content, summarizing it using Amazon Bedrock, and delivering the summary either via API response or by storing it for future retrieval.
Why This Is Needed
- Organizations face information overload with a large number of documents.
- Manual summarization is time-consuming and inconsistent.
- AI enables faster, accurate, and scalable content summarization.
- Amazon Bedrock provides easy access to powerful foundation models without managing infrastructure.
- Helps improve decision-making by delivering quick, reliable insights.
Architecture Overview
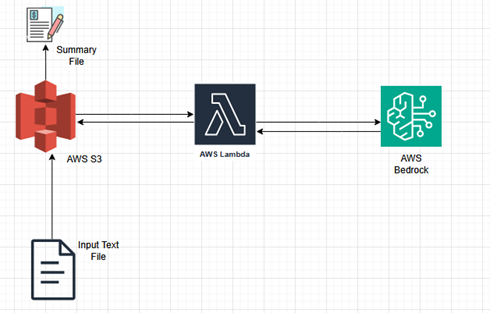
- Uploads a document (TXT, PDF, or DOCX) to an S3 bucket.
- S3 triggers a Lambda function.
- Extracted content is passed to Amazon Bedrock for summarization (e.g., Claude 3 Sonnet).
- The summary is stored in Amazon S3.
- Lambda returns a response confirming successful summarization and storage.
AWS Services We Used
- Amazon S3: Used to upload and store original documents like TXT, PDF, or DOCX files.
- AWS Lambda: Handles the automation logic, triggered by S3 upload, it parses content and invokes Bedrock.
- Amazon Bedrock: Provides powerful foundation models (Claude, Titan, or Llama 3) for generating document summaries.
- IAM Roles: Securely manage permissions across services to ensure least-privilege access control.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Create an S3 Bucket
- Navigate to AWS Console → S3 → Create Bucket
- Example bucket name: kunaldoc-bucket
Note: Use the US East (N. Virginia) region (us-east-1) since Amazon Bedrock is not available in most of the regions (e.g., not available in Ohio).
- Inside the bucket, create two folders:
- uploads/ – to store original documents (TXT, PDF, DOCX)
- summaries/ – to save the AI-generated summaries.

Step 2: Enable Amazon Bedrock Access
- Go to the Amazon Bedrock console.
- Navigate to Model access from the left menu.

- Select and enable access to the foundation models to be used, such as:
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet (I used)
- Meta Llama 3
- Anthropic Claude
- Wait for the status to show as Access granted (this may take a few minutes).
Note: Make sure you’re in the same region as your Lambda function (e.g., us-east-1 / N. Virginia).

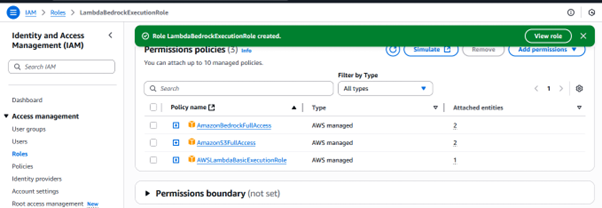
Step 3: Set Up IAM Role for Lambda
- Go to IAM > Roles > Create Role
- Choose Lambda as the trusted entity type
- Attach these AWS managed policies:
- AmazonS3FullAccess
- AmazonBedrockFullAccess
- AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
- Name the role something like: LambdaBedrockExecutionRole
This role allows Lambda functions to securely access S3, invoke Amazon Bedrock, and write logs to CloudWatch.
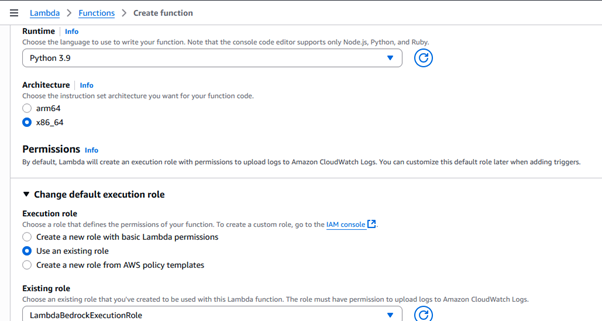
Step 4: Create the Lambda Function
- Go to AWS Lambda > Create Function
- Set the Function Name: docSummarizerLambda (I used that)
- Select Runtime: Python 3.9
- Choose the Execution Role you created earlier.
(LambdaBedrockExecutionRole)
- Upload your code:
- I added the lambda_function.py code to the GitHub repo.
- Dependencies (like lxml, PDF) are also included in the same GitHub repo.
- Download the dependencies zip file to your local machine and attach it as a Lambda Layer during Lambda configuration.
This Lambda function handles document parsing, model invocation, and storing the generated summary
Step 5: Set S3 as the Trigger for Lambda
- Go to your Lambda function → Configuration → Triggers → Click “Add trigger”
- Select Source as S3
- Choose the S3 bucket you created earlier (which contains uploads/ and summaries/ folders)
- Set the Event type – PUT
- Under Prefix, enter: uploads/
- Leave Suffix empty (optional)
- Click “Add” to finalize the trigger.
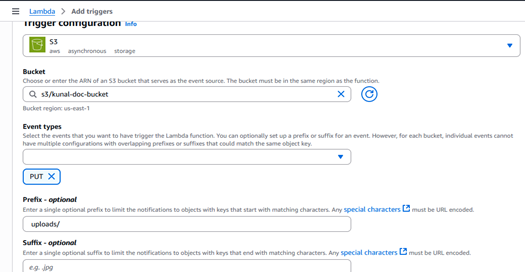
This ensures your Lambda function is automatically invoked whenever a new file is uploaded to the uploads/ folder in your bucket.
Step 6: Add Lambda Layer for Dependencies
To include external Python libraries (like lxml, pdfminer.six, or python-docx), create a Lambda Layer:
-
Download the dependencies ZIP
- Clone or download the dependencies folder from the GitHub repo.
-
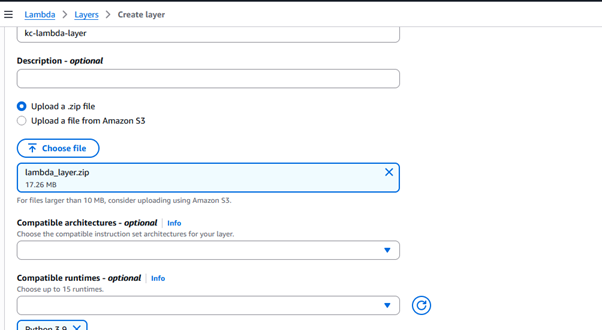
Create the Layer
- Go to AWS Lambda > Layers > Create layer
- Name it (e.g., kc-lambda-layer)
- Upload the ZIP file you downloaded
- Set the compatible runtime to Python 3.9
- Click Create
-
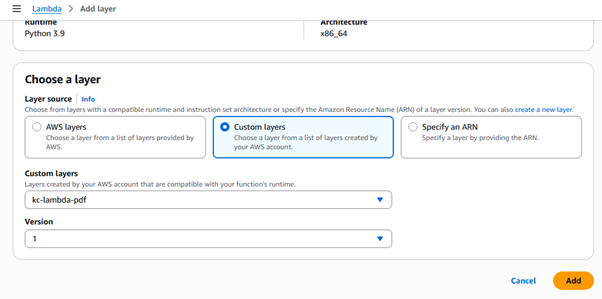
Attach Layer to Lambda Function
- Open your Lambda function
- Go to Configuration > Layers
- Click Add a layer > Custom layers
- Select the one you just downloaded
- Click Add
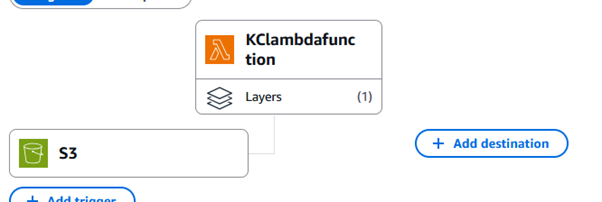
The final version of the Lambda function is shown below:
Step 7: Upload a Document
- Navigate to S3 > uploads/ folder.
- Upload your document
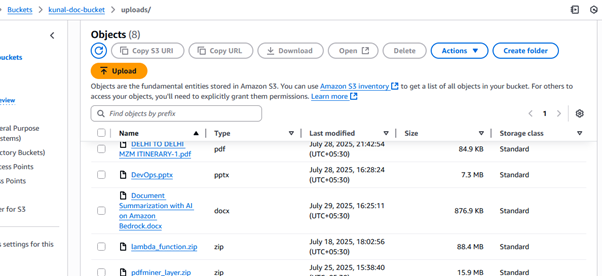
Once uploaded, the Lambda function is automatically triggered and performs the following actions:
- Sends content to Bedrock for AI-based summarization.
- Saves the summary in the summaries/ folder in the same S3 bucket.
Sample data of Document Summarization with AI on Amazon Bedrock file:

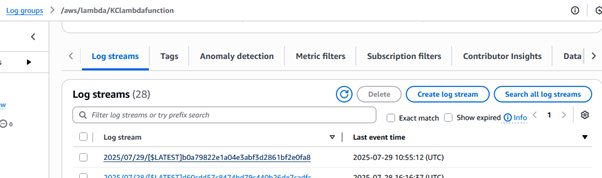
Step 8: Monitor Lambda Logs in CloudWatch
Debug or verify your Lambda execution:
- Go to your Lambda Function in the AWS Console.
- Click on the Monitor tab → then View CloudWatch Logs.
- Open the Log stream to inspect detailed logs and execution steps.
This helps track any errors or view how the document was processed and summarized.
Step 9: View Output Summary
- Navigate to your S3 bucket → open the summaries/ folder.
- Download the generated file (e.g., script_summary.txt).

Results
We can see that the summary for the document summarization with the AI.txt file is successfully generated and saved as document summarization with_summary.txt inside the summaries/ folder.

Conclusion
With this serverless workflow, you’ve built an automated document summarization pipeline using Amazon S3, Lambda, and Bedrock. This solution allows us to upload documents in various formats (TXT, PDF, DOCX) and receive concise summaries stored securely in S3 without manual intervention. It’s scalable, cost-effective, and ideal for document-heavy workflows like legal, academic, or business reporting.
We can further enhance it by adding an API Gateway to fetch summaries on demand or integrating DynamoDB for indexing and search.


Document summarization with AI is a major leap forward, especially for handling large-scale content efficiently. Excited to see how Amazon Bedrock is enabling more scalable and accurate solutions in this space!
https://epaper.samayajyothi.com/