Introduction
Logging is an essential part of application development, especially in cloud environments where monitoring and debugging are crucial. In Azure Functions, there is no built-in provision to log application-level details into a centralized database, making it challenging to check logs every time in the Azure portal. This blog focuses on integrating NLog into Azure Functions to store all logs in a single database (Cosmos DB), ensuring a unified logging approach for better monitoring and debugging.
Steps to Integrate Logging Framework
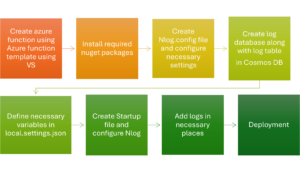
1. Create an Azure Function Project
Begin by creating an Azure Function project using the Azure Function template in Visual Studio.
2. Install Required Nuget Packages
To enable logging using NLog, install the following NuGet packages:
Install-Package NLog
Install-Package NLog.Extensions.Logging
Install-Package Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos
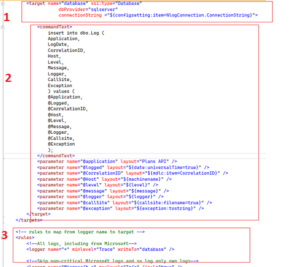
3. Create and Configure Nlog.config
NLog uses an XML-based configuration file to define logging targets and rules. Create a new file named Nlog.config in the project root and configure it with the necessary settings.
Refer to the official NLog documentation for database target configuration: NLog Database Target
Important: Set Copy to Output Directory to Copy Always in the file properties to ensure deployment.
4. Create Log Database
Create an Azure Cosmos DB account with the SQL API.
Sample Cosmos DB Database and Container
- Database Name: LogDemoDb
- Container Name: Logs
- Partition Key: /Application
5. Define Necessary Variables
In the local.settings.json file, define the Cosmos DB connection string.
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "UseDevelopmentStorage=true",
"CosmosDBConnectionString": "AccountEndpoint=https://your-cosmosdb.documents.azure.com:443/;AccountKey=your-account-key;"
}
}

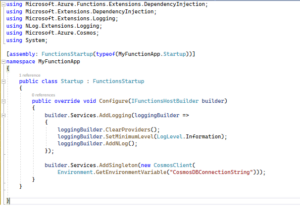
6. Configure NLog in Startup.cs
Modify Startup.cs to configure NLog and instantiate database connection strings and log variables.
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using NLog.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos;
[assembly: FunctionsStartup(typeof(MyFunctionApp.Startup))]
namespace MyFunctionApp
{
public class Startup : FunctionsStartup
{
public override void Configure(IFunctionsHostBuilder builder)
{
builder.Services.AddLogging(loggingBuilder =>
{
loggingBuilder.ClearProviders();
loggingBuilder.SetMinimumLevel(LogLevel.Information);
loggingBuilder.AddNLog();
});
builder.Services.AddSingleton(new CosmosClient(
Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("CosmosDBConnectionString")));
}
}
}
7. Add Logs in Necessary Places
To ensure efficient logging, add logs based on the following log level hierarchy:
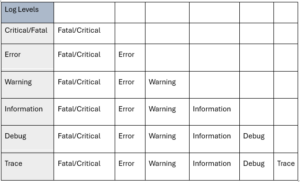
Example Logging in Function Code:
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Azure.Cosmos;
using Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
public class MyFunction
{
private readonly ILogger<MyFunction> _logger;
private readonly CosmosClient _cosmosClient;
private readonly Container _container;
public MyFunction(ILogger<MyFunction> logger, CosmosClient cosmosClient)
{
_logger = logger;
_cosmosClient = cosmosClient;
// Initialize Cosmos DB container
_container = _cosmosClient.GetContainer("YourDatabaseName", "YourContainerName");
}
[FunctionName("MyFunction")]
public async Task Run([TimerTrigger("0 */5 * * * *")] TimerInfo myTimer)
{
var logEntry = new
{
id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(),
timestamp = DateTime.UtcNow,
logLevel = "Information",
message = "Function executed at " + DateTime.UtcNow
};
// Insert log into Cosmos DB
await _container.CreateItemAsync(logEntry, new PartitionKey(logEntry.id));
_logger.LogInformation("Function executed at {time}", DateTime.UtcNow);
}
}
8. Deployment
Once the function is ready, deploy it to Azure Function App using Visual Studio or Azure DevOps.
Deployment Considerations:
- Define necessary environment variables in Azure Function Configuration Settings.
- Ensure Azure Function App Service and SQL Database are in the same network to avoid connection issues.
- Monitor logs using Application Insights for additional diagnostics.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can successfully integrate NLog into your Azure Functions for efficient logging. This setup enables real-time monitoring, structured log storage, and improved debugging capabilities.

