Mark Perterson, VP, Building and Asset Optimization and Stephan Marguet, Executive Director, Real Estate Business Services Citizens’ Services in British Columbia presented an informative session at IBM Think 2018, “Building a Blueprint to Smart Buildings / How to Plan and Prepare for the Future.”
Mark began the session with background and important reasons why smart buildings are important.
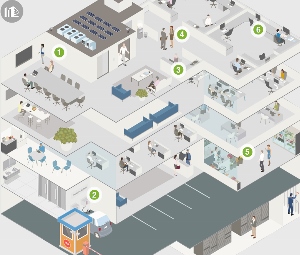
There has been a transformation in the last 5 years to make buildings more fit for purpose. Ultimately buildings need to become more conducive to their purposes and improve occupant experience. An example of increasing the occupant experience is a sensor that conveys the length of cafeteria lines and makes it available to building occupants, allowing them to know when lines are long to avoid peak waiting periods. Additional highlights include:
Five Core Challenges
- Grow in a low growth, digitally disrupted world
- Seek innovation and data leverage as a basis for new growth
- Take-out structural costs for competitiveness and to fund investment in growth
- Win the war for talent to access intelligence and innovation
- Transform enterprise processes and systems to enable growth and competitiveness
Transformer focus is key to achieving exponential improvements in building performance
- Optimizing – Drive outcomes through productivity, efficiency and effectiveness
- Re-engineering – Reduce work steps by adopting new operating procedures and processes
- Transformation – Use insights from data to change how enterprises operate and functions
Building Optimization with IoT – Analytics, sensors and existing systems can improve occupant experience and reduce operations
- Enhance occupant workspace environment and engagement
- Optimize building maintenance and improve services
- Reduce costs and increase operational efficiency
Advanced technology speeds the transformation of building experience
- Foundational – Single source of record to support real estate life cycle
- Developing – Risk reduction, health, safety and automated services with IoT
- Advanced – Deliver cognitive services, e.g. AR/VR
Operational efficiency examples
- Data for heating/cooling
- Automatic surveillance and security
- Streamlined elevators
- Analytics to prevent energy waste
- Secure check-in
- Control water waste
Steve then took over and spoke about how the Ministry of Citizens’ Services in British Columbia manages smart building initiatives.
Smart building investments are in 2 streams which lead to capturing data analytics for continuous recommissioning and fault detection.
- Improving Data
- Automation
- Technology (sensors, zoning)
- Real time energy metering
- IT infrastructure
Example initiatives and ROI were provided
- Infrastructure upgrades and automation to a courthouse built in 1985 lead to a 25% energy savings in 2016
- Proof of concept using WiFi enabled controls allows adjusting HVAC based on detection data
Mark wrapped up the session wrapped up with best practices in building transformation.
- In context – Personable and consumable experiences
- Real-time – Respond dynamically to time sensitive problems
- Intelligent – Adaptable and machine learning
- Instrumented and interconnected – Combine structured and unstructured data
The information in the session was very enlightening to help understand the importance and value of IoT and data in smart buildings.