Machine learning algorithms can seem as strange and scary as an alien attack, but they’re having a massive impact on how search engines like Google evaluate your site and its content. Are you doing what it takes to win at SEO in the machine learning age?
In this episode of our popular Here’s Why digital marketing video series, Perficient Digital’s Eric Enge explains what machine learning is and how it is impacting SEO.
Don’t miss a single episode of Here’s Why. Click the subscribe button below to be notified via email each time a new video is published. Over a half million views on YouTube!
Resources
- The Machine Learning Revolution: What It Is And How It Impacts SEO
- See all of our Here’s Why Videos | Subscribe to our YouTube Channel
Transcript
Mark: Eric, you’ve been studying and following machine learning for some time now, but where did it start for you?
Eric: Back in 2011, I did an interview with Google’s Peter Norvig that opened my eyes to the possibilities of machine learning for search. Peter told me how Google used machine learning to teach their Google Translate program new languages. I immediately recognized that Google could and probably would use that technology for many other things, including improving its search ranking algorithms.
So, I set about to learn as much as I could about machine learning, and even took a full course on Coursera by Andrew Ng of Stanford University, and he’s actually the Chief Scientist at Baidu, by the way. And I learned enough from that to begin experimenting with my own machine learning programs. And since then, I’ve actually taken more courses as well.
What Is a Machine Learning Algorithm?
Mark: That’s awesome. Well, let’s back up for a moment though and make sure we understand what machine learning is. Can you explain that?
Eric: Sure. First, there are basically two kinds, supervised machine learning and unsupervised machine learning.
First, let’s look at the supervised machine learning. So, at a most basic level, think of the supervised version as a series of equations created to fit a known set of data. Let’s say, you want to try to predict housing prices. You could start with the simplest data set like this one we’re showing right now.
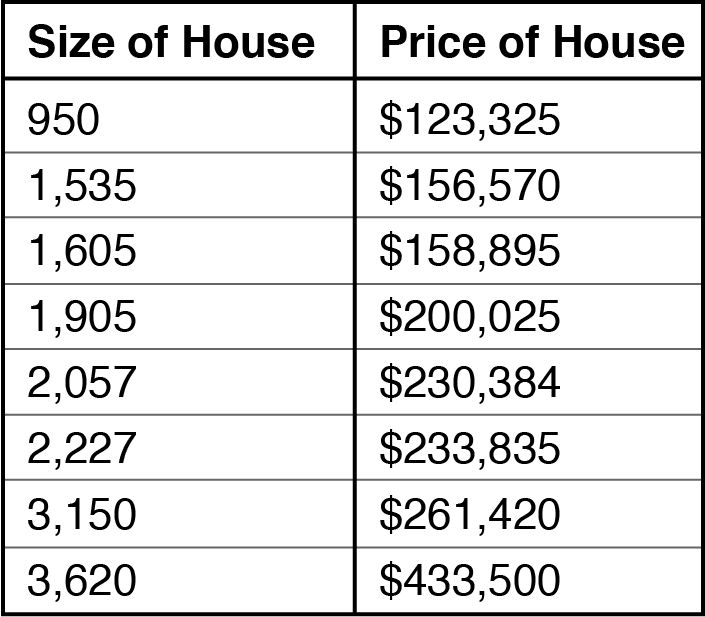
The data, by the way, is fictitious but will serve the purpose of this example. We can then plot the data on a graph. No surprise here. As the size of a house increases, the price goes up, but this model’s way too simplistic.
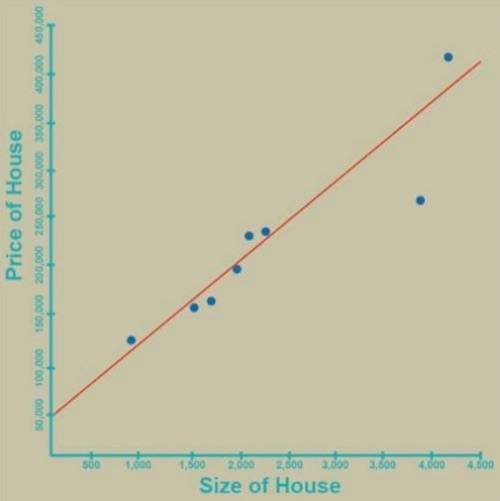
And so, there are many factors that go into the price of a house such as lot size, number of bedrooms, number of bathrooms, etc. Now a simple straight line graph won’t do to give us the data that we need, so we have to design weights to each of these new factors. For example, the number of bedrooms or bathrooms are factors, but not as important as the lot size, and we haven’t begun to weigh in other factors such as the location.
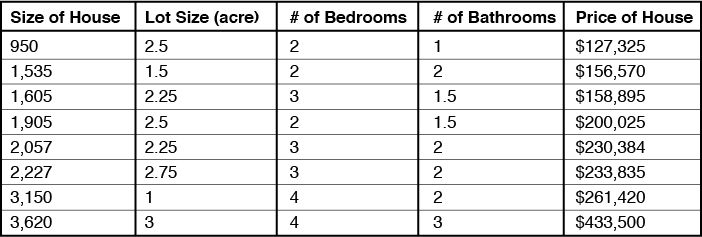
There’ll be a big difference between a house in Austin, Texas, and, say, downtown New York. So, as you can see, our solution is becoming a lot more complex.
Supervised machine learning can be really good for solving these kinds of problems. We’d set up large sets of data to begin with and we’d call that training data, and design an algorithm to make a prediction based on that data. We then look at the results to see how they match up with the real world, adjust our algorithms as needed, and feed in new training data along the way. This process is what we call supervised machine learning.
Mark: What is unsupervised machine learning?
Eric: Unsupervised machine learning comes into play when we don’t have training examples to work with. In such a case, you try to build an algorithm that can recognize patterns and similarities among diverse objects. For example, you might start with data that looks like this.
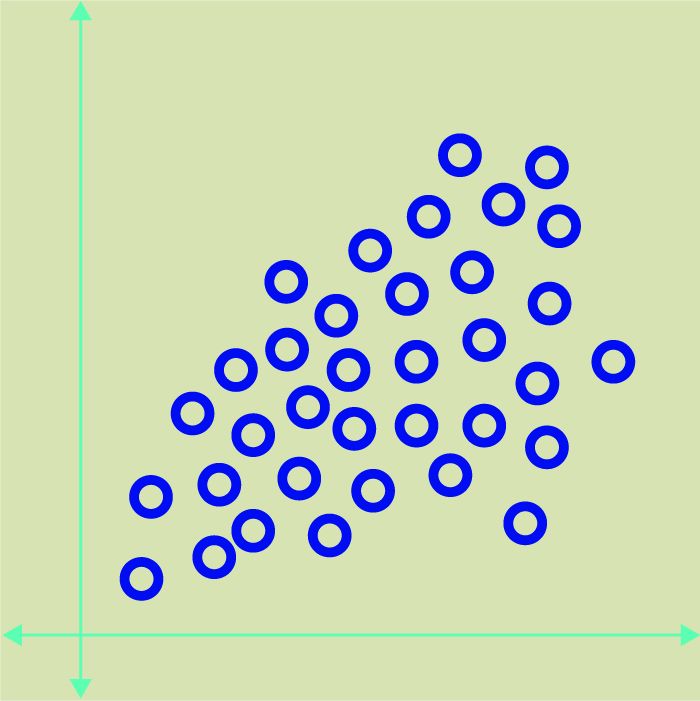
The algorithm will then attempt to analyze this data and figure out how to group the data points together based on common characteristics. Perhaps, in this example, all of the red X points in the following chart share similar attributes.
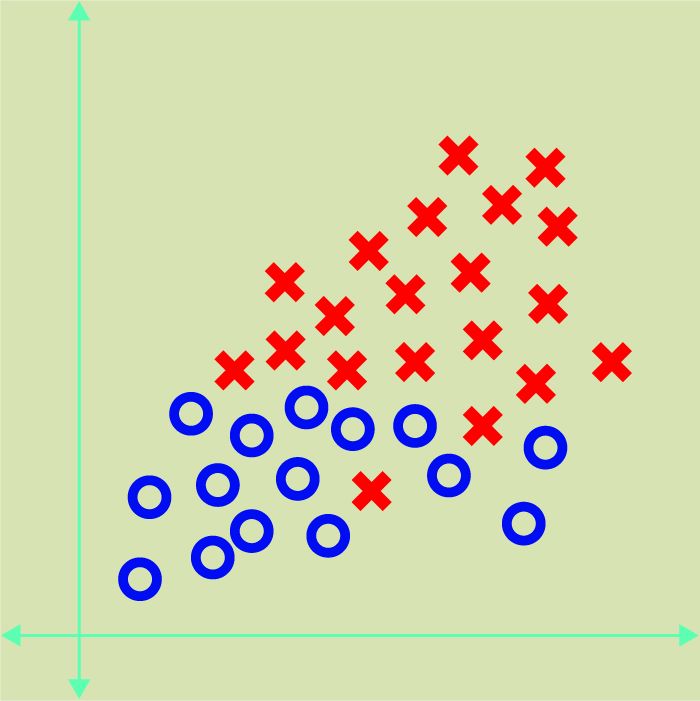
So, unlike supervised machine learning where you’re providing training data that includes examples of real-world results and telling it some simple ways to give weights to try to predict those results, with unsupervised machine learning, the algorithm is left to figure out the patterns all by itself, and it’s designed to do its own testing with constant feedback loops to intervally improve its ability to understand the data and group those data sets together accurately.
Machine Learning and SEO
Mark: How does all that apply to SEO then?
Eric: Never forget that Google has a high incentive to keep improving the quality of its search results as there’s a strong correlation between user satisfaction of those results and Google’s revenue from search ads. These days, Google faces stiff competition in search not only from other traditional search engines such as Bing, but from newer players like Amazon, Apple’s Siri, and Microsoft’s Cortana, and even Facebook. So, Google needs to continually improve the quality and usefulness of its search results. But doing that, at the massive scale of the entire internet, is too daunting a task for human engineers to solve alone, and this is where machine learning algorithms actually enter into the picture.
Mark: Given that, what do SEOs need to do? What should they actually put into practice?
Eric: Knowing that Google’s getting better and better at assessing content quality and user satisfaction at massive scale, those two things must be treated as ranking factors for all your pages. So, here are some questions to ask yourself.
- Does your page meet the intent of a large percentage of the people who will visit it?
- Are you providing the help users might need to select the right product or learn to use it?
- Do users get good suggestions of related products they might need?
- Are there gaps in your content in the page? Are there details or related information you could put on it to flush out the content more?
- Does your page provide a higher quality of experience than the pages of competitors?
- Do you have a strategy for measuring page performance and how to improve it?
Mark: Thanks, Eric. Our readers can check out your article on the impact of machine learning on SEO to get even more insights.
Don’t miss a single episode of Here’s Why. Click the subscribe button below to be notified via email each time a new video is published.
See all of our Here’s Why Videos | Subscribe to our YouTube Channel

