How do Oracle Forms work in R12?
What components are involved??
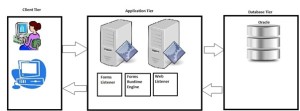
Oracle forms server works based on 3 Tier Architecture. A tier is a logical collection of services running on more than one machine.
Client Tier:
The client browser connects to the form server using the forms client Applet which is running on the local machine. Forms client applet is a collection of Java Archive files (JAR).
Application Tier:
Application tier mainly has 2 components web listener and forms server.
• Forms server :
o Maintains all user interfaces and database connection for thin client.
o Caches data which is needed by forms thin client.
o Uses HTTP, HTTPS and TCP/IP protocols to communicate with the thin client.
• Web Listener
o Sends and receives request for the browser which is running the Jinitiator.
Database Tier:
• Stores all the data required for the forms thin client.
How it works??
1. Browser sends request to HTTP Listener.
2. Web server receives the request.
o If request is referring to a static file then the file will be retrieved from storage.
o If request is referring to CGI Script then
Static CGI : Retrieve from storage and execute the file.
Dynamic CGI : Checks for the available server from load balancing server. Load balancing server basically monitors the current load in all forms server. Forms server runs a thin client of load balancing server to keep the load balancing server informed about the load.
3. HTTP Listener sends a HTML page to the browser.
o HTML file has a tag
Client browser and JRE Version
Below table lists out the JRE version for the corresponding client browser and the information is available in the Oracle support “Deploying JRE (Native Plug-in) for Windows Clients in Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12 (Doc ID 393931.1)” .Also any form related issues are addressed in the same Oracle Doc ID.
64 Bit version
| Consortium | Number of Members | Premier Financial Services Members | Leader(s) | Start Date | Focus/Goal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R3CEV | 84 | DTCC, American Express, Bank of America Merrill Lynch, Wells Fargo, Citigroup, TD Bank, BBVA, Bank of New York Mellon, Northern Trust, HSBC, Barclays | R3, CEV | 2014 | General-purpose platform and technology to design and deliver advanced distributed ledger technologies to the financial services market. |
| Digital Asset Holdings | 15 | Deutsche Borse, J.P. Morgan, DTCC, ABN AMRO, Goldman Sachs, Santander, Citi, IBM | DAH | 2014 | Capital markets – post-trade settlement. Building distributed, encrypted straight through processing tools to improve efficiency, security, compliance, and settlement speed. |
| Hyperledger Project | 142 | J.P. Morgan, Barclays, Deutsche Bank, Wells Fargo, UBS, BBVA, Bank of New York Mellon | Linux Foundation, IBM, Cisco, Intel, SWIFT, DAH | 2015 | General purpose blockchain. Open source collaborative effort based on IBM’s Fabric codebase, which was created to advance cross-industry blockchain technologies. It is a global collaboration that includes leaders in finance, banking, the internet of things (IoT), supply chain, manufacturing, and technology. The Linux Foundation hosts Hyperledger as a Collaborative Project under the foundation. |
| Ethereum | 116 | J.P. Morgan, Santander, BNY Mellon, BBVA, Bank of New York Mellon | Microsoft, Intel | 2017 | Considering a more distributed approach to self-management rather than the more traditional leadership structure adopted by competing blockchain consortia like R3CEV and Hyperledger. Offers smart contract features that contain a virtual machine, executing peer-to-peer contracts using a cryptocurrency known as Ether. |
| Ripple | 75 | UBS, Standard Chartered, Santander, CIBC, Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation (SMBC), MUFG, Mizuho | Google, IDG Capital Partners | 2012 | Payments. A real-time gross settlement system (RTGS), currency exchange and remittance network by the company of the same name. The Ripple Transaction Protocol (RTXP) or Ripple protocol is built upon a distributed open-source Internet protocol, consensus ledger and native currency called XRP (ripples). |
| Kinakuta | 35 | Ethereum Foundation | Microsoft, ConsenSys | 2016 | Working group dedicated to improving smart contracts security. |
32 Bit Version
| Function | Current Process | Future Process | Impacted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security and Digital Identity – Compliance (KYC) | The Know Your Customer (KYC) regulation is an integral part of global anti-money laundering (AML) efforts. Compiling and maintaining these databases is expensive for financial services; this can lead to duplication of effort and can delay transactions. | If digital identities are recorded on a blockchain shared ledger, an individual can add devices to their identity and add authorization to transact on their behalf. Verifiable and robust identities, cryptographically secured blockchain technology could provide a single digital source of ID information, allowing for the seamless exchange of documents between banks and external agencies. This would likely result in automated account opening and reduced resources and costs, while maintaining the legally required privacy of data. | All financial services firms, payment card networks, regulators |
| Cross-border Payments | Cross-border payments use SWIFT messaging. Fees are leveraged by multiple intermediaries. | BBVA cleared a real money transfer between Spain and Mexico in minutes. One-fee Smart contracts can be coded to reflect any data-driven business logic. For example: •Cross-border transactions •Digitalizing letters of credit •Loan repayments | Consumer banks, commercial banks |
| Clearing & Settlement | Centralized clearing and settlement for all financial instruments. Settlement can take from days to weeks, depending on the complexity of the transaction. | Settlement can be done in minutes using blockchain. A fundamental advantage of a distributed ledger system, in which no single company has control, is that it resolves problems of disclosure and accountability between individuals and institutions whose interests are not necessarily aligned. It gives each member of the network far greater and timelier visibility of the total activity. DTCC has already proven that complex post-trade events inherent to credit default swaps (CDS) can be managed with distributed ledger technology in a permissioned, distributed, peer-to-peer network. | Investment banking, asset management, corporate banking, hedge funds, ForEx trading, clearinghouses, central banks, regulators |
| Transfer of Ownership (Contracts, Titles) | Transferring title of a property or negotiating contractual terms for financing, funding and loads is a long and onerous process with multiple intermediaries, include the legal profession. | Securities based on payments and rights that are executed according to predefined rules can be written as smart contracts. A smart contract is any contract that can automatically enforce itself without the need for a trusted intermediary. Any contract can be a smart contract if the terms of the contract can be automated. The blockchain assures that everybody is seeing the same thing at the same time, which negates the need for trust. | All banks, legal profession, real estate industry, regulators |
| Asset Management | Each party in the trade lifecycle (e.g., broker dealers, intermediaries, custodians, clearing and settlement teams) currently keeps its own copy of the same record of a transaction, creating significant inefficiencies and room for error. | Blockchain technology would provide an automated trade lifecycle in which all parties to the transaction would have access to the exact same data about a trade. This would lead to substantial infrastructural cost savings, effective data management and transparency, faster processing cycles, minimal reconciliation, and a reduced need for brokers and intermediaries. | Asset management banks, broker-dealers, custodians |
| Smart Assets (Supply Chain/Trade Finance) | Primary pain points for supply chain firms are: no visibility of payments, long payment schedules, demand management. | Blockchain provides a system of trusted records that addresses all three. Digitizing letters of credit and bills of lading facilitates a smart asset tracking system. Tracking assets that are rich in data can be turned into information for corporate clients. | Financing firms, supply chain industry |
| Lending | Multiple intermediaries and fees for bank loans, mortgages, credit card debt, government bonds, muni bonds, asset-back securities | Both loan and collateral can be stored in a blockchain. A smart contract can automatically revoke access to the collateral if the terms of the loan are broken. Debt can be issued, traded and settled on the blockchain. Improves small business lending and lending for the unbanked (Approx. 2bn – World Bank). | Commercial banking, consumer banking, payment card network, money transfer services, telecommunications, regulators |
| Funding | Funding and investing in an asset, IPOs, dividends, capital appreciation, rental income | Peer-to-peer financing, recording of corporate actions, automatic payment of dividends, smart contracts for title registries. Contracts that monitor the performance of digital or non-digital assets can also be used as futures, forwards, swaps, and options. | Investment banking, corporate banking, real estate, legal |
| Insurance | Managing risk, derivatives, insuring assets | Decentralized markets for insurance, more transparent derivatives | Insurance, risk management, brokerages, corporate banks, clearinghouses, regulators |
| Governance | Accounting for value | A distributed ledger will mean real-time audit and financial reporting capabilities. Transparency of the blockchain improves regulatory management. | Audit, asset management, regulators, banks |
| Recording and storing transactions and custody | Centralized recording and storage of financial assets, currencies, commodities for all types of accounts | Cryptographic mathematical equations and immutable blockchain secures recording and storing of all transactions. Will reduce need for typical financial services accounts (brokerage, checking, savings, etc.). | Consumer banks, Investment banks, brokerages, asset management, regulators |